The Divi Blog Module
How to add, configure and customize the Divi blog module.
The Divi Blog Module is actually much more than just a way to display your blog posts. It can display posts, pages, media, projects, and products in a full-width layout or a masonry-style grid layout, with thousands of design options available at the click of a button! Making the Divi Blog Module the ideal way to display content on your website.
View A Live Demo Of This Module
How to Add the Divi Blog Module to Your Page
Before you can add the Divi Blog module to your website, you’ll need to have the Divi theme installed on your WordPress website. Learn how to install the Divi theme on your WordPress website here. Once you have the Divi theme installed and activated, we can begin using the features and functionalities of Divi.
Add a Page and Load the Divi Builder
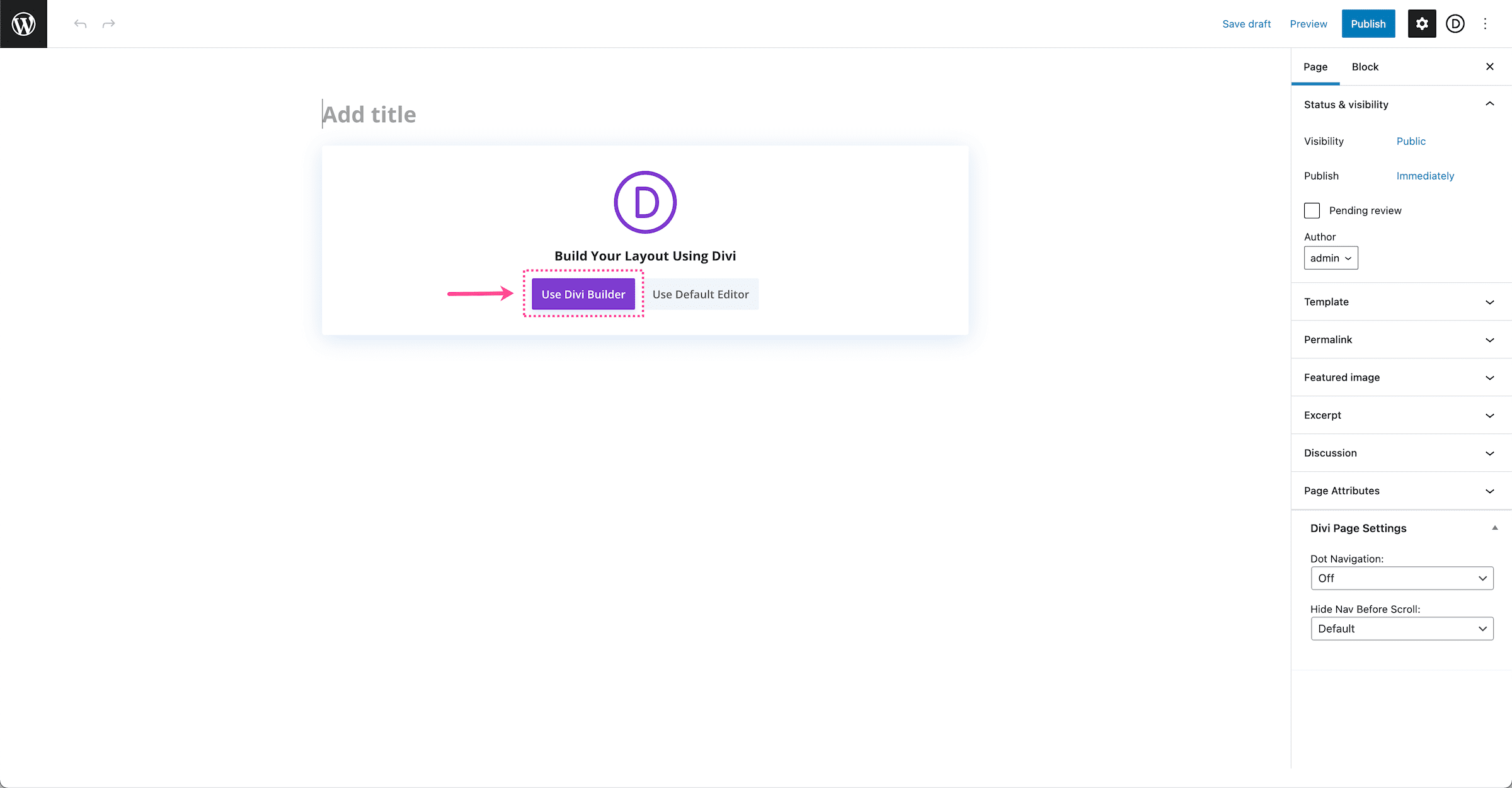
To get started, add a new page to your website. By default, the Standard Gutenberg Editor loads whenever a new post or page is added to WordPress. To load the Divi builder on any post or page, click the purple button underneath the page title that says “Use The Divi Builder.”
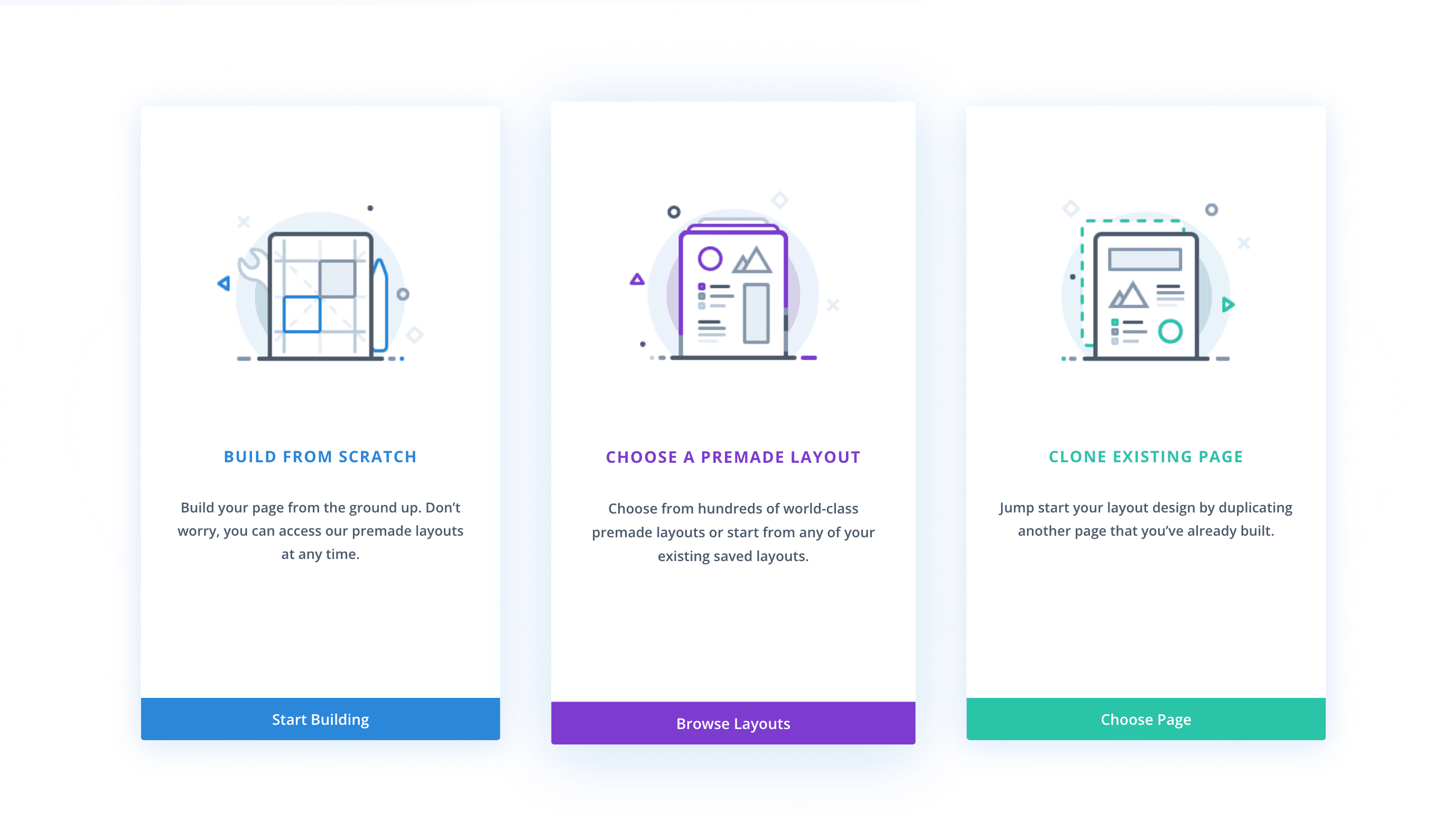
Once clicked, this will reload the page with the Divi Visual Builder. As your page reloads, you’ll notice three options that come up: Build From Scratch, Choose A Premade Layout, and Clone An Existing Page.
Build from Scratch
This option loads the Divi Builder with a blank page design. Choose this option if you’d like to start your page design from scratch.
Choose a Premade Layout
This option allows you to choose from our large library of pre-designed Divi layouts. You can choose from premade layouts by Divi, pre-made layouts you’ve designed and saved to your Divi Library, and existing pages on your website that you can clone.
Clone an Existing Page
This option allows you to copy another page design on your website and use it for the page you’re editing. Select this option if you’d like to load an exact copy of an existing page that you’ve already designed on your website.
Select, Build from Scratch.
Add the Blog Module
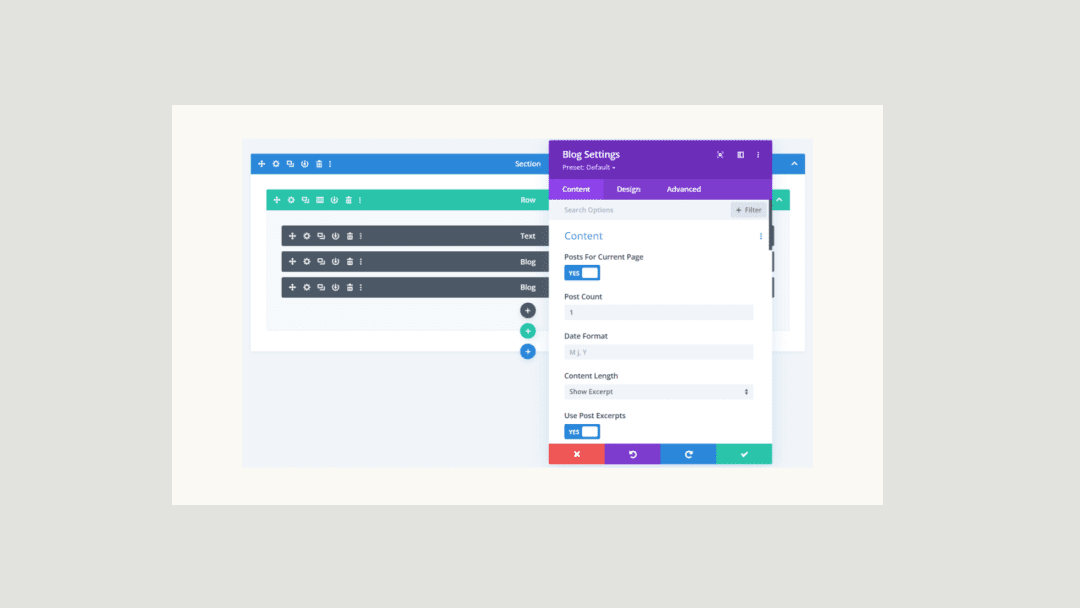
When you load the Visual Builder, Divi automatically adds a section and a row. You can learn more about how to modify and customize sections here and rows here. Once the section, row, and columns are set up, click on the grey “+” icon inside the row. This brings up the Divi Module Library which contains all the modules included with the Divi theme. Scroll down to “Blog” and click on it to load the blog module.
Note: This module library is also searchable via the search bar at the top of the module library window.
All Blog Module Options Explained
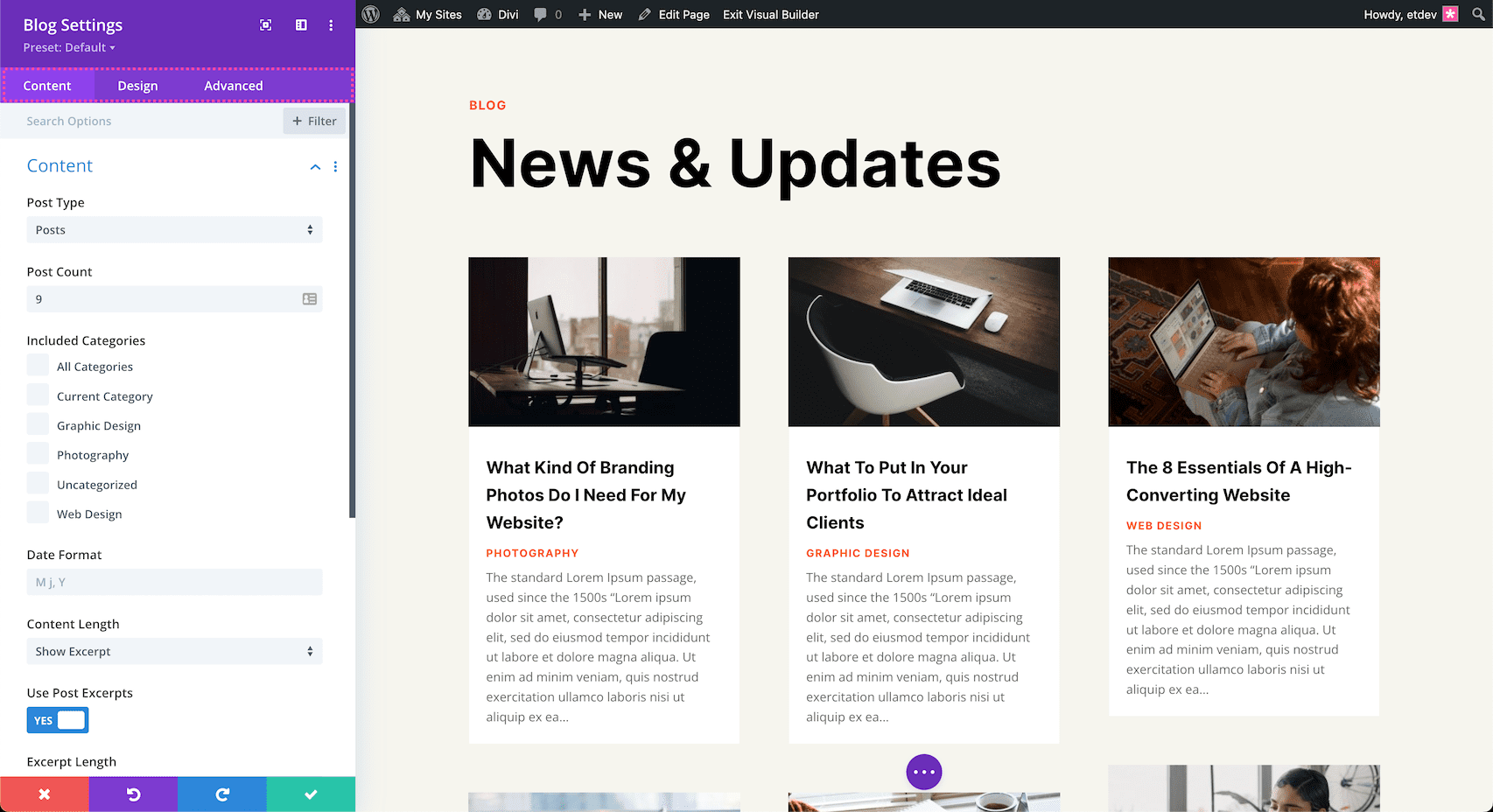
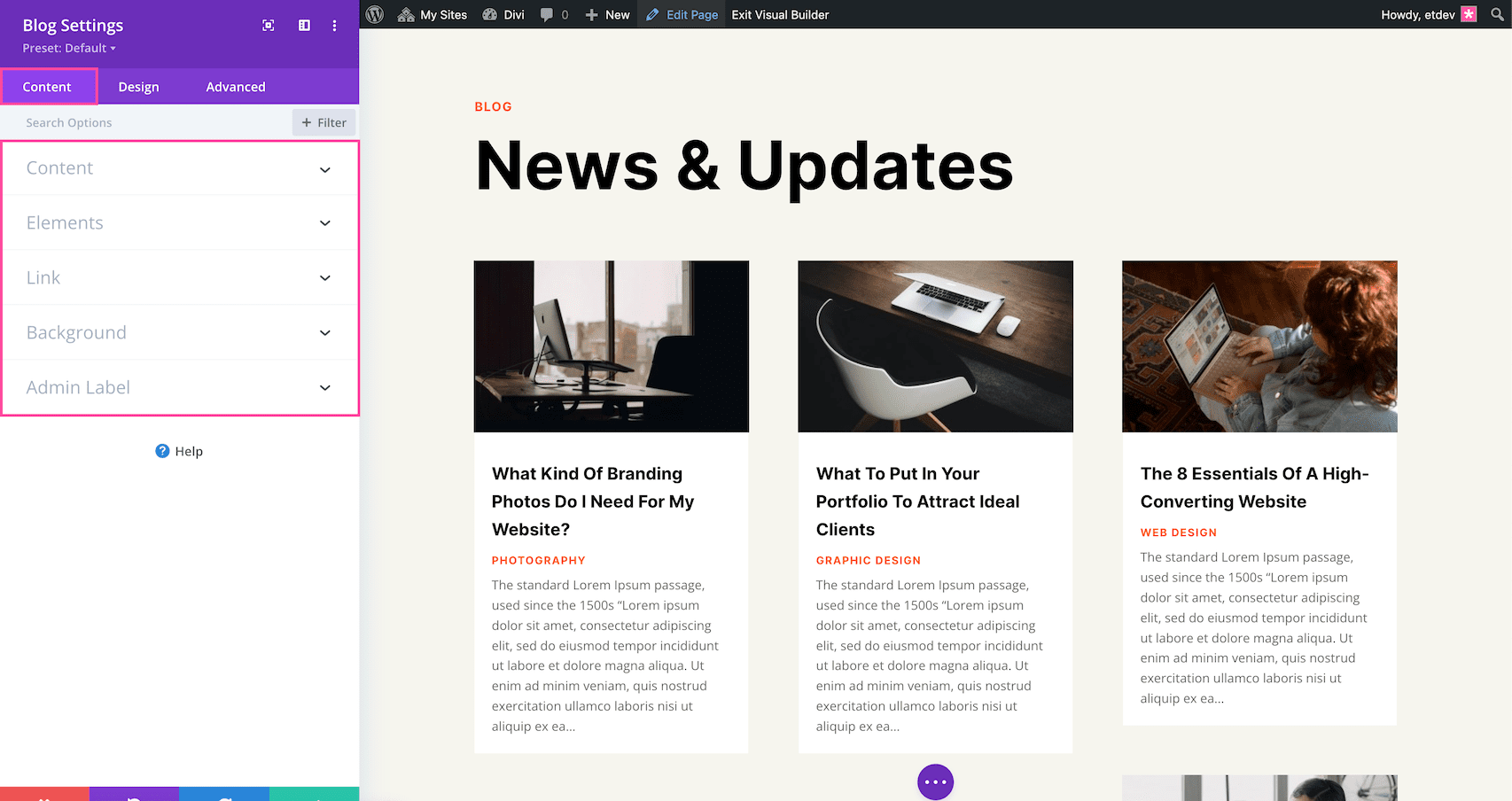
Once you’ve added the Blog module, the module settings automatically pop up. This is where all of the content and design styles for this module are configured. These settings are organized into three groups via the tabs at the top of the module: Content, Design, and Advanced.
Content
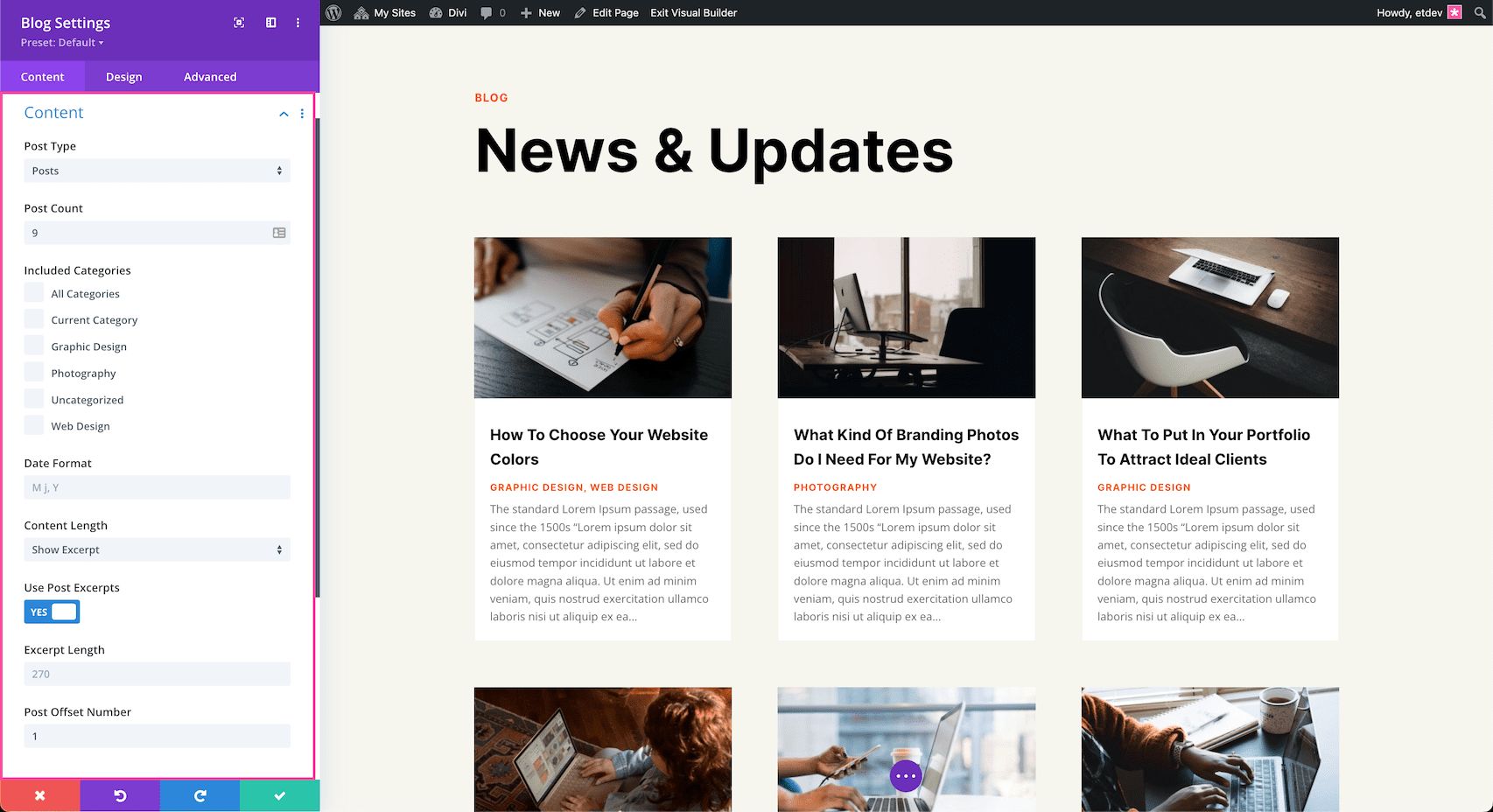
Inside this tab, you’ll find the content options available for the Blog module.
Content
Inside this tab is where you control the content of the blog module. You can use the blog module to display blog posts, pages, media, projects, and products.
Select Post Type
Click the dropdown to select what type of content you want to be displayed.
Content Options for Blog Posts:
- Post Count – Type the number of posts you would like to be displayed here.
- Included Categories – Select the categories you would like to be displayed. By default, all categories are displayed. You can pick as many as you’d like.
- Date Format – This is where you can change how the date displays. M=month, j=date, and Y=year. Keep in mind, that these letters are case-sensitive. The “j” must always be lowercase in order to display the day as a numerical number. The “M” and the “Y” can be either uppercase or lowercase. When the “M” is lowercase then the month will display as a numerical value. When it’s uppercase, it will display as a shortened text version of the month. When the “Y” is uppercase it will display the full four digits of the year, and when it’s lowercase it will display as the last two digits of the year.
- Content Length – Click the dropdown and select either “Show Excerpt” or “Show Content” to determine the length of the content you want displayed.
- Use Post Excerpts – Disable this option if you want to ignore manually defined excerpts and have them always generate automatically.
- Excerpt Length – By default, excerpts are 270 characters in length. If you want to lengthen or shorten that number, type in a numerical value here.
- Post Offset Number – Choose the number of posts you would like to offset or pass over. So if you’d like the blog feed to start with the third most recent blog post, you would put a number 3 here.
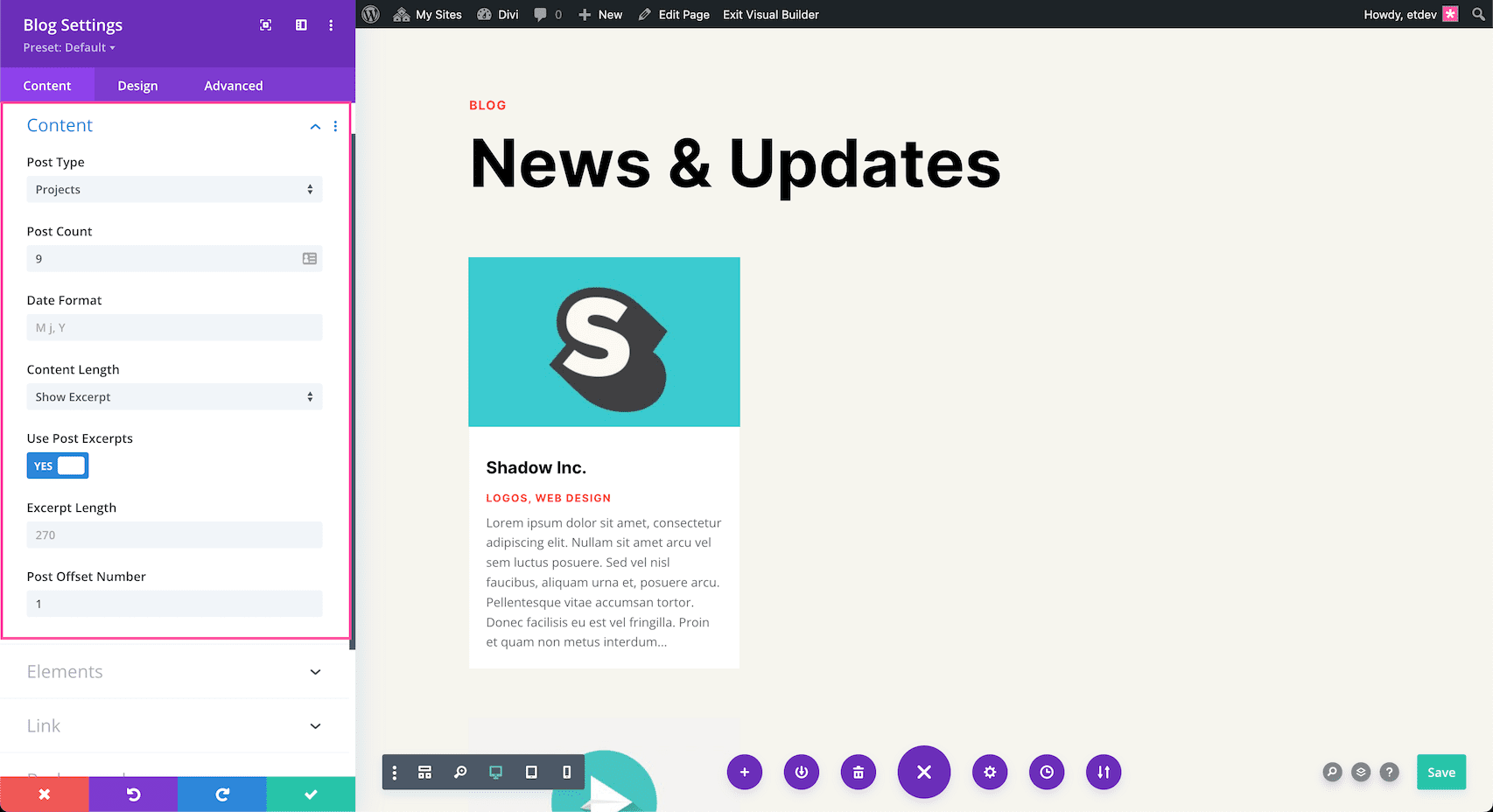
Content Options For Pages, Media, Projects, and Products:
- Post Count – Type the number of posts you would like to be displayed here.
- Date Format – This is where you can change how the date displays. M=month, j=date, and Y=year. These letters are case-sensitive. The “j” must always be lowercase in order to display the day as a numerical number. The “M” and the “Y” can be either uppercase or lowercase. When the “M” is lowercase then the month will display as a numerical value. When it’s capitalized, it will display as a shortend text version of the month. When the “Y” is uppercase it will display the full four digits of the year, and when it’s lowercase it will display as the last two digits of the year.
- Content Length – Click the dropdown and select either “Show Excerpt” or “Show Content” to determine the length of the content you want displayed.
- Use Post Excerpts – Disable this option if you want to ignore manually defined excerpts and have them always generate automatically.
- Excerpt Length – By default, excerpts are 270 characters in length. If you want to lengthen or shorten that number, type in a numerical value here.
- Post Offset Number – Choose the number of posts you would like to offset, or pass over.
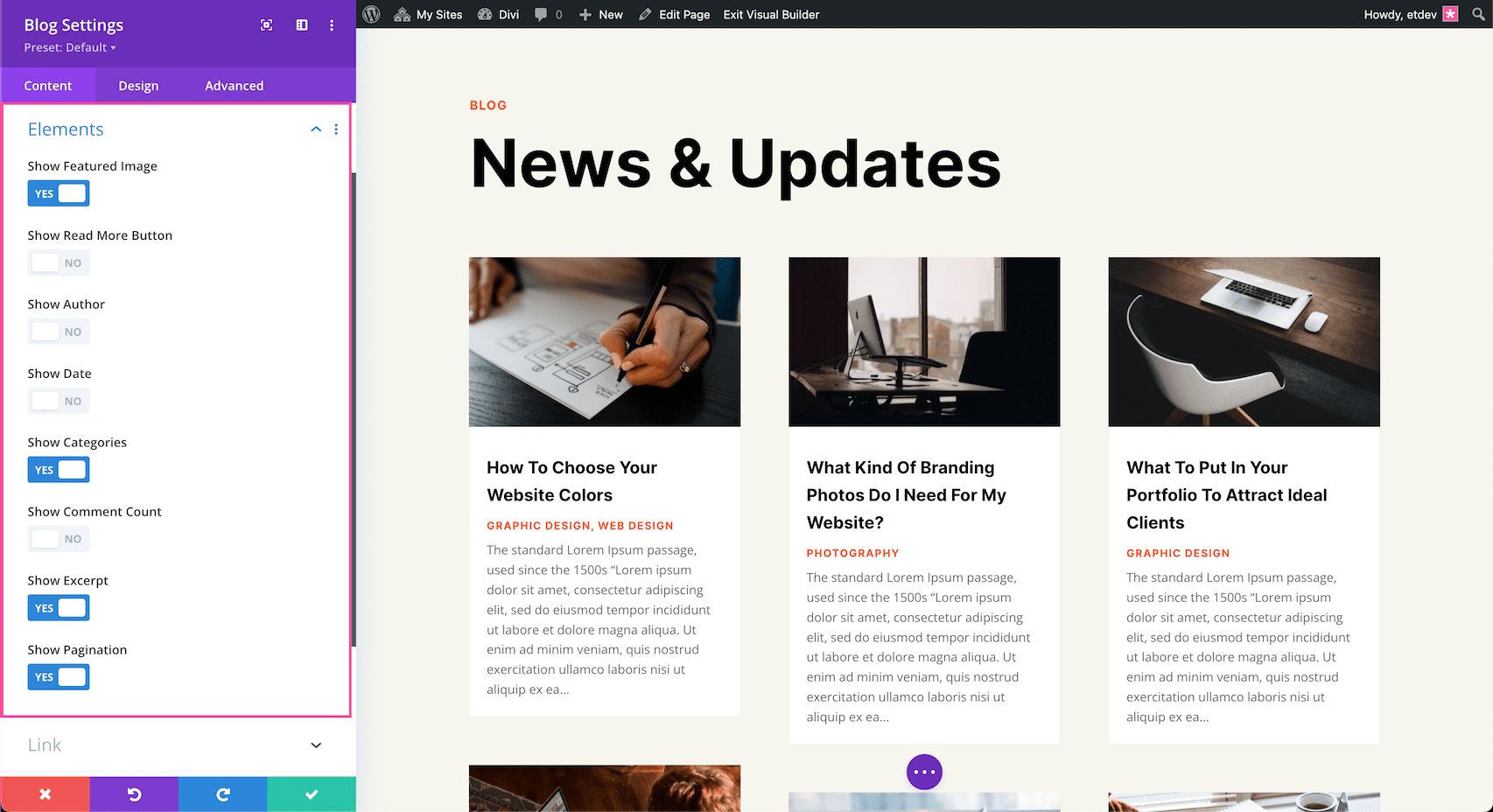
Elements
Regardless of the post type, the element options are:
- Show Featured Image – Toggle this open “yes” or “no” to show or hide the featured image.
- Show Read More Button – Toggle this open “yes” or “no” to show or hide the read more button.
- Show Author – Toggle this open “yes” or “no” to show or hide the author’s name in the meta text.
- Show Date – Toggle this open “yes” or “no” to show or hide the post date in the meta text.
- Show Categories – Toggle this open “yes” or “no” to show or hide the categories in the meta text.
- Show Comment Count – Toggle this open “yes” or “no” to show or hide the comment count in the meta text.
- Show Excerpt – Toggle this open “yes” or “no” to show or hide the post excerpt.
- Show Pagination – Toggle this open “yes” or “no” to show or hide the pagination link at the bottom of the module.
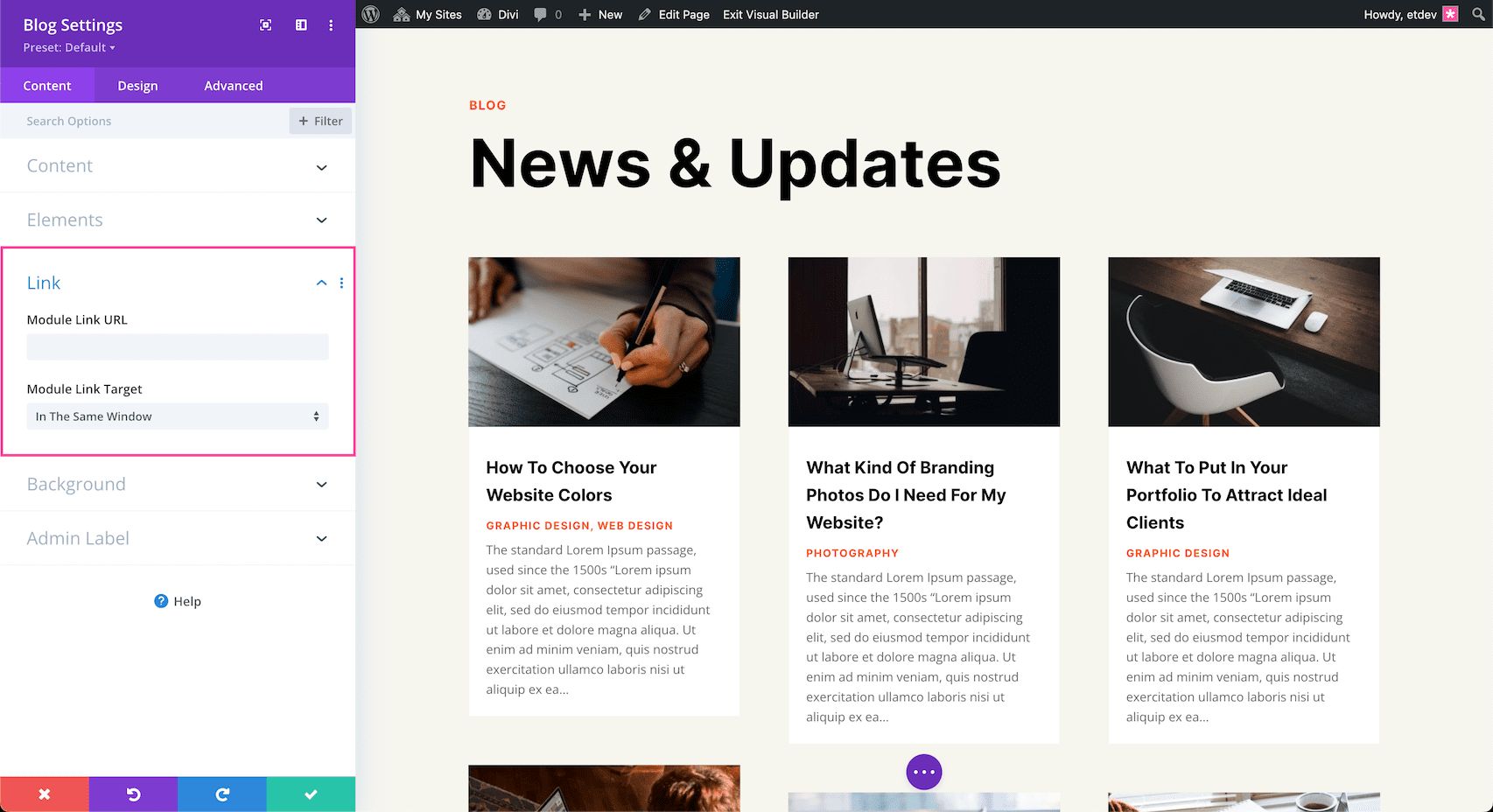
Link
If you would like to apply a clickable link to the entire module, you can do so here.
- Module Link URL – Paste the URL of the link you would like to apply to this module here. This makes the entire module clickable and when clicked it will direct visitors to the URL pasted here.
- Module Link Target – Defining a link target determines whether the link, when clicked, opens in a new tab or in the same window. Choose “In The Same Window” if you want the link to open in the same window and click “In The New Tab” if you would like that link to open in a new tab. By default, “In The Same Window” is selected.
Background
This is where you can add a background color, gradient, image, video, pattern, or mask to this module.
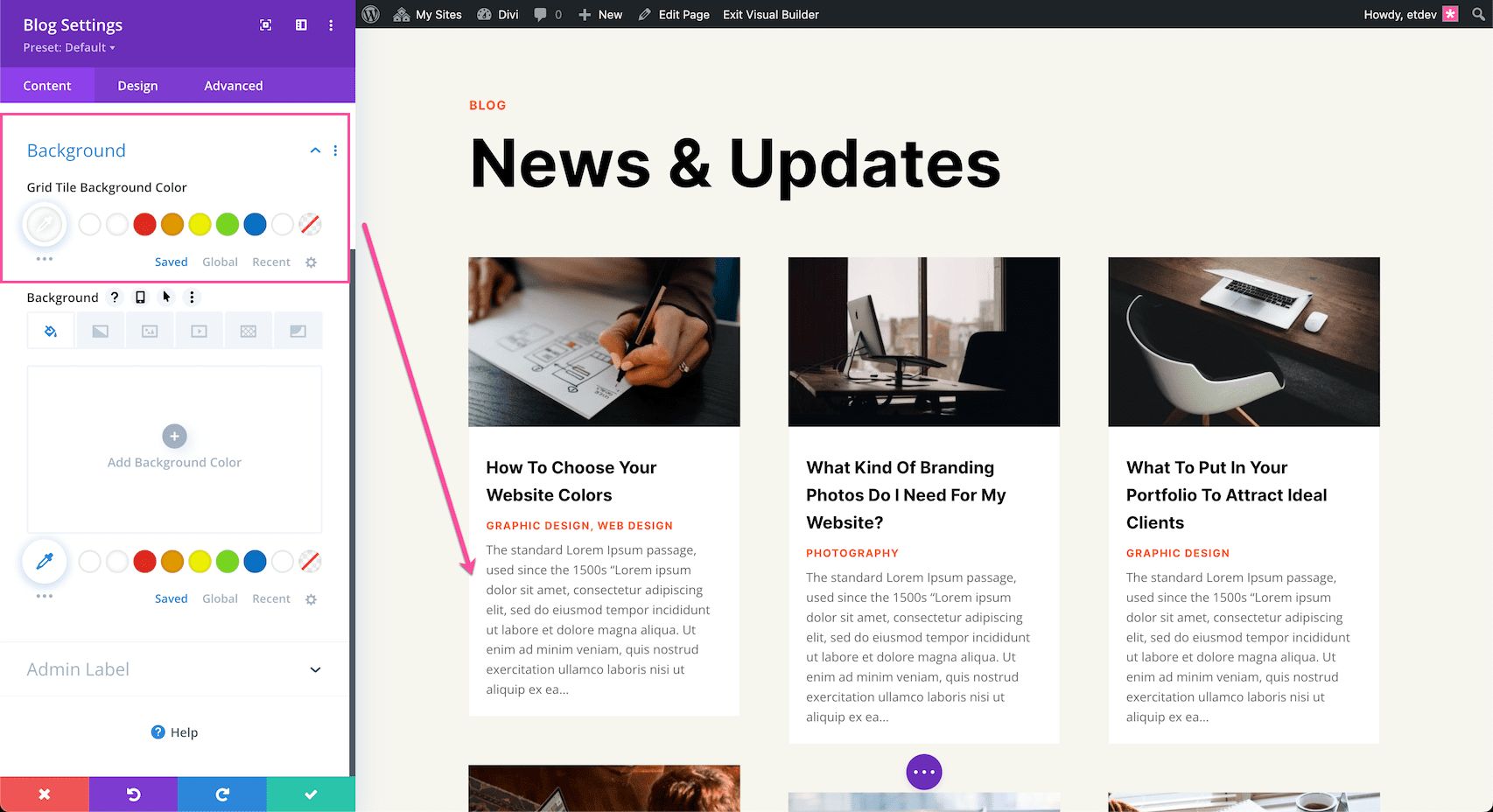
Grid Tile Background Color
In this module, you have the ability to add a background color to the blog post tiles. To do so, select a color from your site’s color palette or use the eyedropper icon to find a new color. This option only applies to the blog post grid tiles.
How to Add a Background Color
To add a background color to the entire module, click the first tab, the paint bucket. Click “Add Background Color” and choose from your site’s color palette or use the eyedropper icon to find a new color.
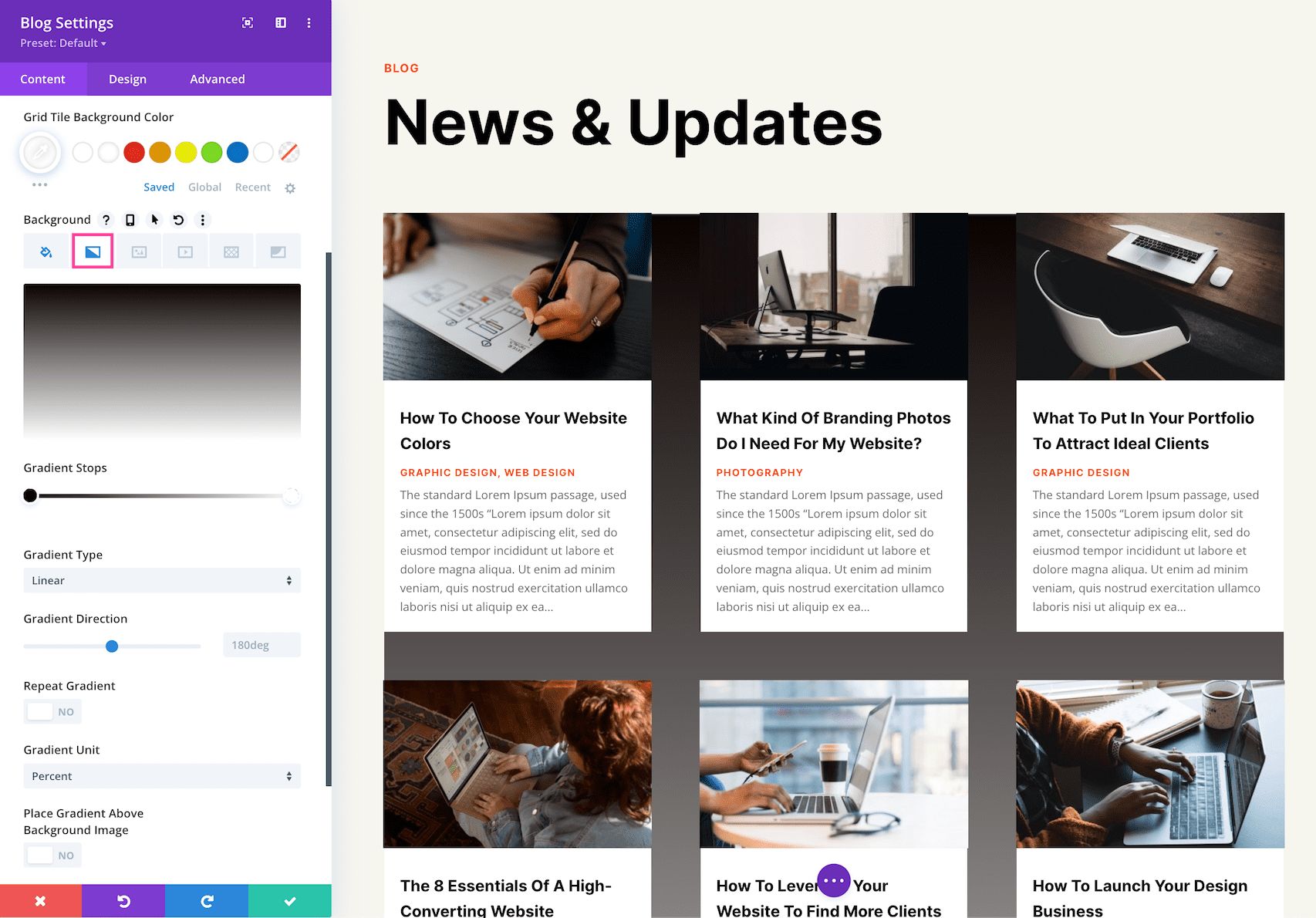
How to Add a Background Gradient
To add a background gradient, click the second tab, the gradient tab, then click “Add Background Gradient.”
To change the gradient colors, click on the gradient stops and select a color from your site’s color palette or use the eyedropper icon to choose a new color. Gradient stops allow you to add more colors to the gradient. Simply click anywhere on the range slider to add a new stop.
- Gradient Type – You can change the gradient type by clicking the dropdown menu and selecting the gradient type you’d like.
- Gradient Direction – You can change the direction of the gradient by dragging the range slider or typing in a numerical value.
- Repeat Gradient – Toggle this option to “yes” if you’d like the gradient to repeat.
- Gradient Unit – The gradient unit changes how the gradient stop points are calculated. Select the dropdown to change the unit.
- Place Gradient Above Background Image – If you have a background image applied, then you can choose to place the gradient above the background image by toggling this option to “yes”.
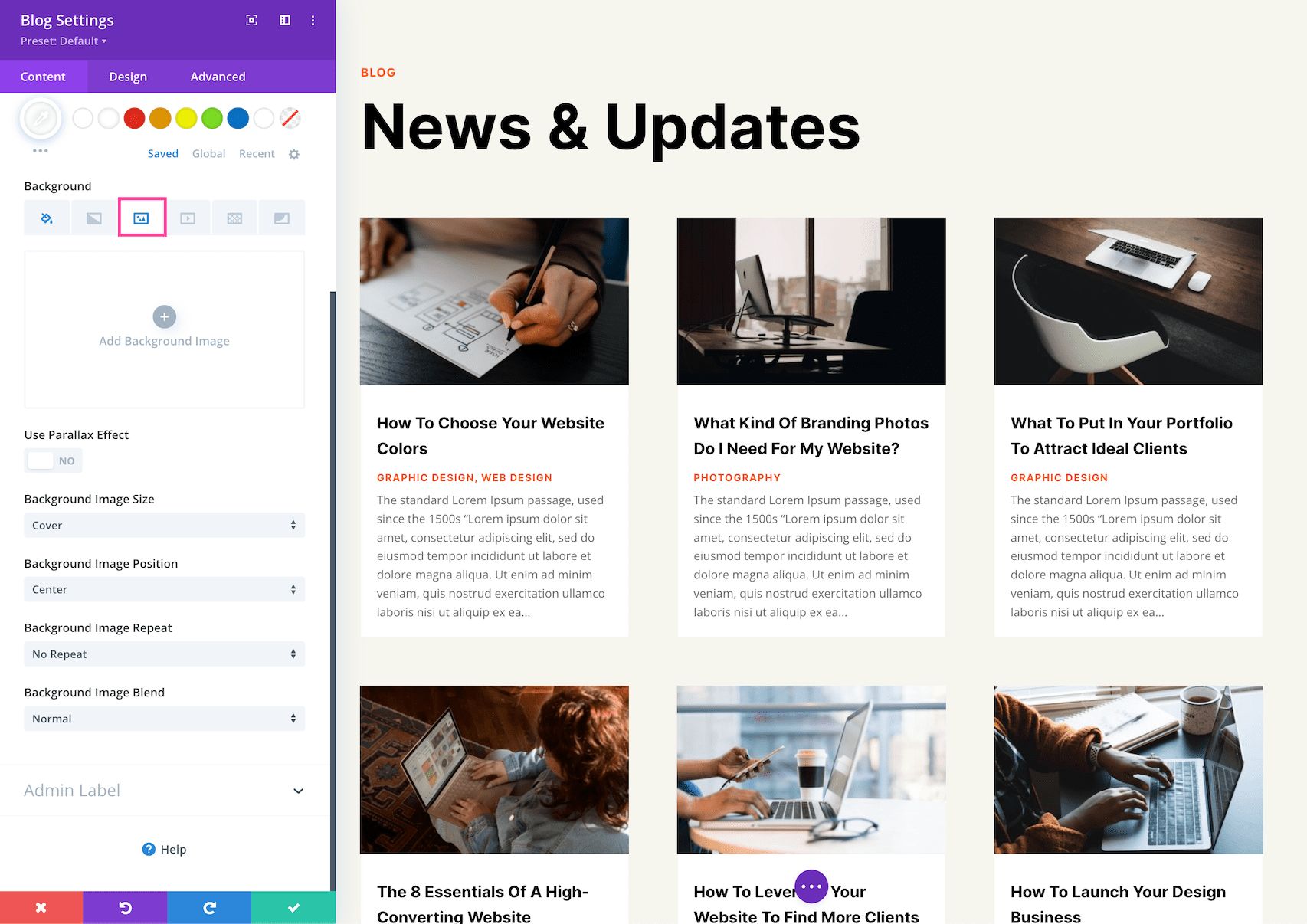
How to Add a Background Image
To add a background image, click the third tab, the image tab. Then, click the gray “+” sign to bring up the media library where you can select an already uploaded photo from your library or upload a new one.
- Use Parallax Effect – To apply a parallax effect to the image (where the image scrolls faster than the foreground content, giving the illusion of a 3D effect) then toggle this option to “on.” By default, this setting is set to “off.”
- Background Image Size – Choose the size of your background image by selecting a size from the dropdown menu.
- Background Image Position – Choose the position of the background image by selecting a position from the dropdown menu.
- Background Image Repeat – Choose if and how the background image repeats by selecting an option from the dropdown menu.
- Background Image Blend – Choose how the background blends with other layers in the module by selecting an option from the dropdown menu.
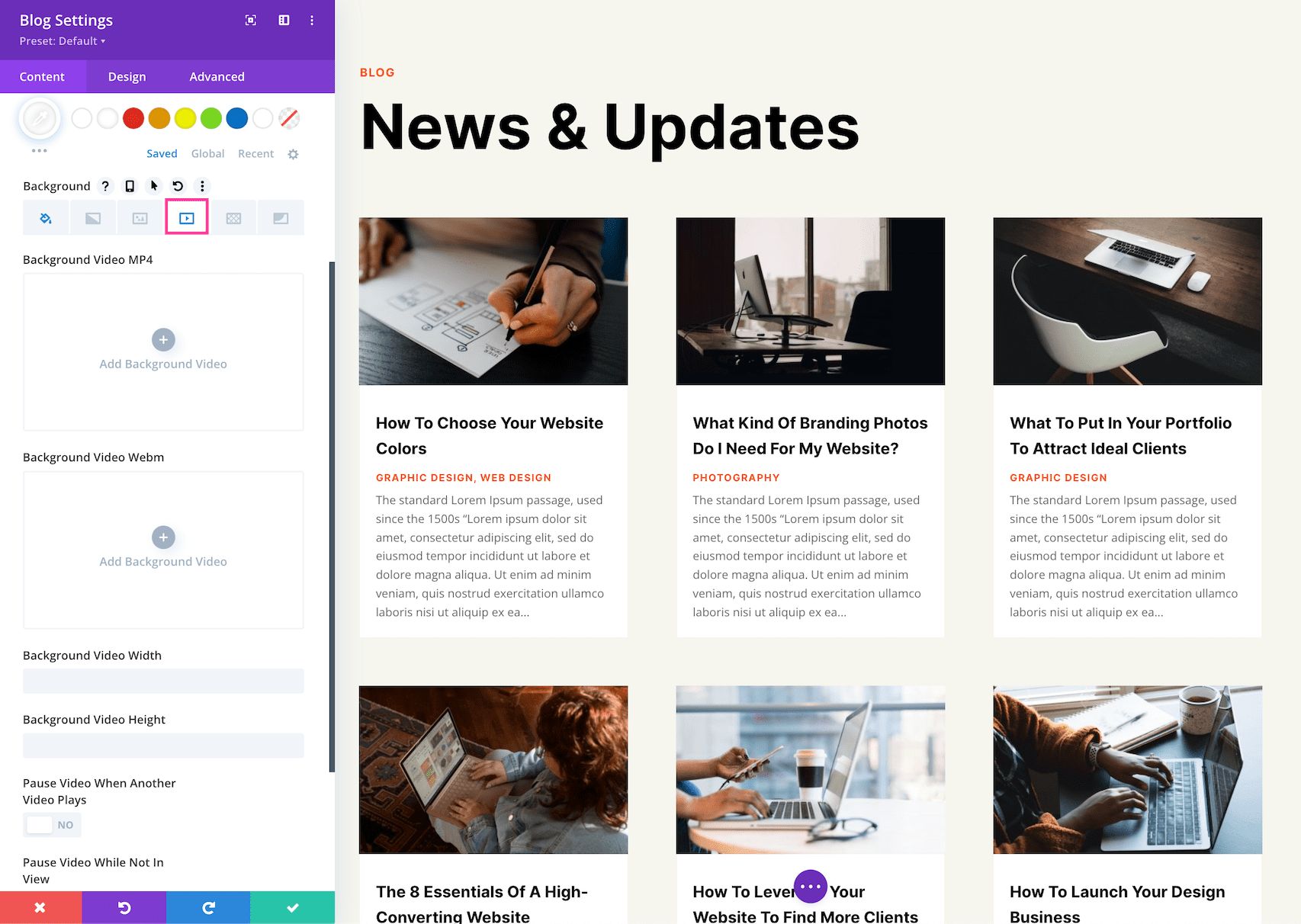
How To Add a Background Video
To add a background video, click the fourth tab, the video tab. Click the gray “+” sign to bring up the media library, where you can select an already uploaded photo from your library or upload a new one.
- Mp4 vs Webm. – We recommend uploading both an mp4 version and webm version of the video because not all browsers support webm video formats. Uploading both file types ensure your video will play on all devices and browsers.
- Background Video Width – Set the width of the video by typing in a numerical value.
- Background Video Height – Se the height of the video by typing in a numerical value.
- Pause Video When Another Video Plays – If you’d like the background video to pause when another video is playing, toggle that option to “yes.” By default, the video will pause when not in view. If you’d like the video to continue playing, toggle this option to “no.”
How to Add a Background Pattern
To add a background pattern, click the 5th tab, the pattern tab, then click “add background pattern.” Choose the pattern type you want from the dropdown.
- Pattern Color – Select the pattern color from your site’s color palette or use the eyedropper icon to find a new color.
- Pattern Transform – This is where you can transform the pattern horizontally, vertically, rotate it, or invert it.
- Pattern Size – Pattern size is where you can select the pattern size: the actual size, cover, fit, stretch to fill or custom size. If you select custom size, the following options will appear: pattern width and pattern height. Drag the range slider or type in a numerical value to define those options.
- Pattern Repeat Origin – Here you can select the origin from which the pattern repeats.
- Pattern Horizontal and Vertical Offset – You can also adjust the horizontal and vertical offsets for the pattern.
- Pattern Repeat – Here you can choose how the pattern repeats – horizontally, vertically, and more.
- Pattern Blend Mode – This defines how the pattern layer interacts with the layers beneath it. Select from one of the 16 blend modes available from the dropdown.
How to Add a Background Mask
To add a background mask, click the 6th tab, the mask tab and then click “add background mask”. Select the mask type you want via the dropdown menu.
- Mask Color – Choose the mask color from your site’s color palette or use the eyedropper icon to find a new color.
- Mask Transform – Here you can transform the mask horizontally, vertically, rotate it, or invert it.
- Mask Aspect Ration – Here you can set the aspect ratio of the mask. The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of its width to its height.
- Mask Size – This is where you can select the mask size: the actual size, cover, fit, stretch to fill, or custom size. If you select a custom size, the following options will appear: mask width and mask height. Drag the range slider or type in a numerical value to define those options.
- Mask Blend Mode – This defines how the mask layer interacts with the layers beneath it. Select one of the 16 blend modes available from the dropdown.
Admin Label
The Admin Label is where you can give the module a name only visible to you in order to assist in keeping things organized and easy to understand on the back end. By default, the admin label will be the name of the module. You can change the text of the admin label to reflect what you’d like.
Design
Inside this tab, you’ll find all the design styles and options for the Blog module.
Layout
Select the layout you want for the blog module here – fullwidth or grid.
- Fullwidth – Select this option if you’d like the content to display fullwidth with the projects displayed one after the other.
- Grid – Select this option if you’d like the content to display as a grid. By default, this displays as a 3-column grid.
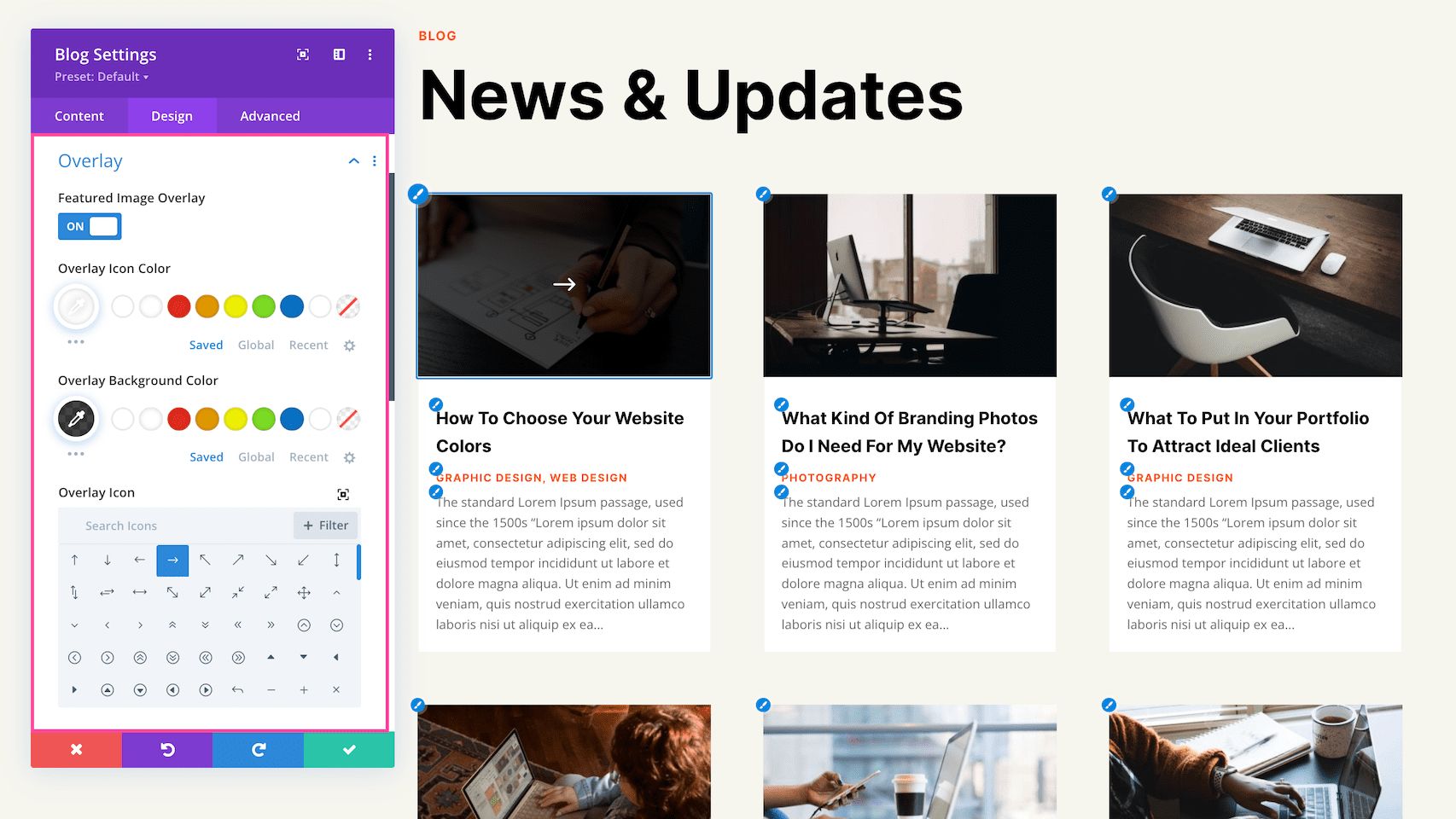
Overlay
- Featured Image Overlay – If you would like to apply an overlay color to the featured image on hover then toggle this option to “yes.” When you have this option set to “yes” then the options below will appear.
- Overlay Icon Color – Choose the color of the icon here. Select from your site’s color palette or click the eyedropper icon to find a new color. If you would like just the overlay background to display and not the icon, set the icon to be transparent by clicking the transparent icon all the way to the right on the color palette line.
- Overlay Background Color – Choose the color of the image overlay here. Select from your site’s color palette or click the eyedropper icon to find a new color.
- Overlay Icon – Select the icon you want to use here.
Image
This is where you can style the featured image.
- Image Rounded Corners – If you would like to round the corners of the image, type in a numerical value. The higher the number, the rounder the corners will be. The corner values are automatically linked (as seen by the highlighted blue chainlink in the middle) however if you’d like to have different values for each corner, simply click the blue chainlink to unlink the values. If the values are automatically linked that means they will always have the same value and update automatically if one value is changed.
- Image Border Styles – This is where you can add a border to the image. You can add a border to all sides of the image, or to individual sides (top, right, bottom, and left).
- Image Border Width – This is where you set the width of the border. For a thicker border, increase the number. The border width must be at least 1px in order to show.
- Image Border Color – This is where you can pick the color of the border. You can select a color from your default site color palette already displayed, or click on the eyedropper icon to find a new color.
- Image Border Style – Here you can select what style of border you’d like: solid, dashed, dotted, double, groove, ridge, inset, outset, or none.
- Image Box Shadow – Choose the style of shadow you want to be applied to the image. By default, no shadow is applied.
- Box Shadow Horizontal Position – Controls the horizontal positioning of the image box shadow.
- Box Shadow Vertical Position – Controls the vertical positioning of the image box shadow.
- Box Shadow Blur Strength – Controls shadow blur strength the image box shadow. The higher the number, the more blur.
- Box Shadow Spread Strength – Controls the spread strength of the shadow on the image.
- Shadow Color – Choose the color of the image shadow.
- Box Shadow Position – Choose the position of the shadow applied to the image – an inner shadow or an outer shadow.
- Image Hue – Adjusts the hue of the image.
- Image Saturation – Adjusts the saturation of the image.
- Image Brightness – Adjusts the brightness of the image.
- Image Contrast – Adjusts the contrast of the image.
- Image Invert – Inverts the color of the image
- Image Sepia – Controls the level of sepia tone applied to the image.
- Image Opacity – Controls the level of opacity (transparency) of the image.
- Image Blur – Controls the blurriness of the image.
- Image Blend Mode – The Blend Mode refers to how the module blends with the layers beneath it. By default, “normal” will be selected.
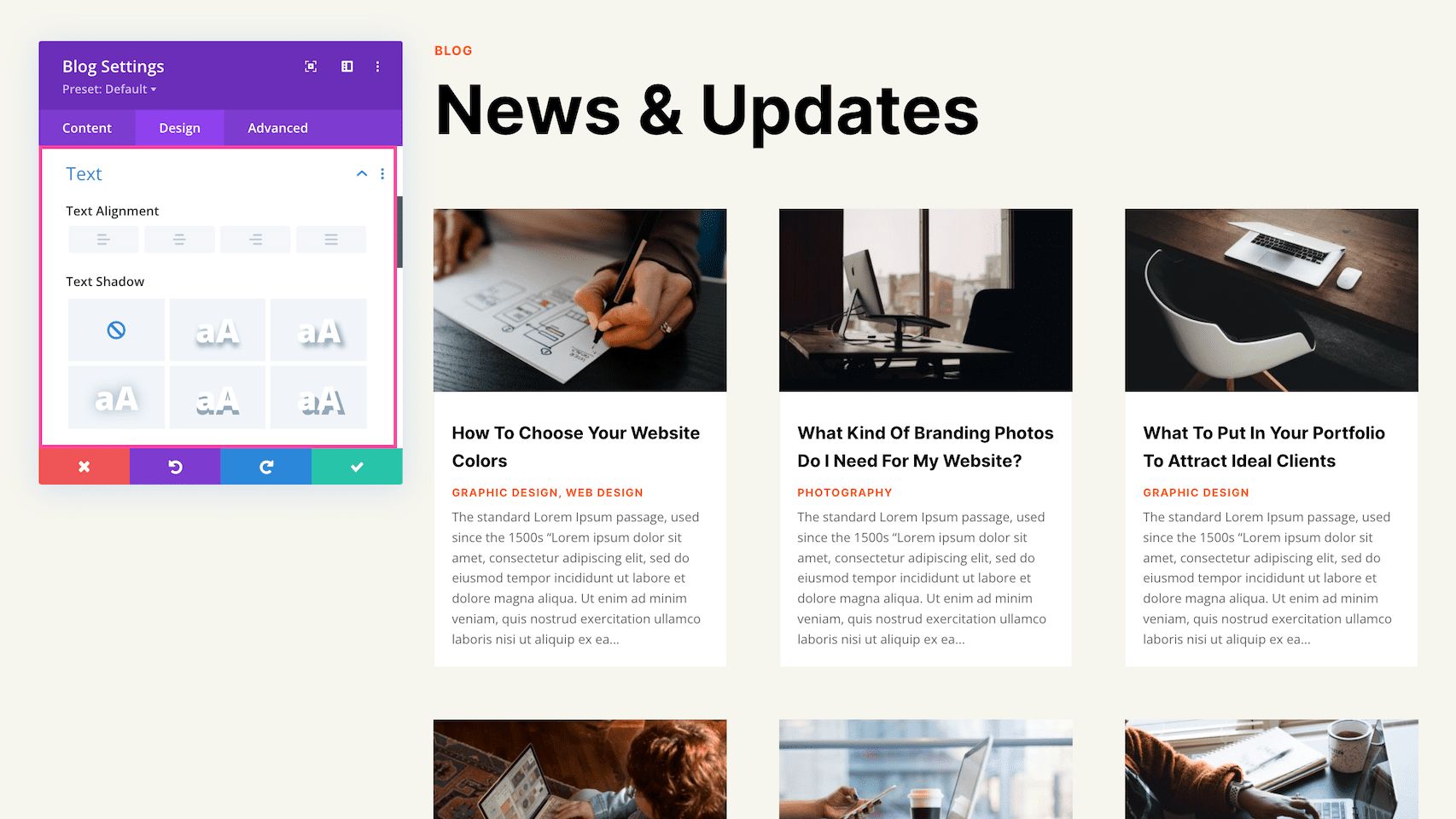
Text
This sets the overall text styles for this module; however, you can set specific styles of specific text in other toggles like Title Text, Body Text, Meta Text, Read More Text, and Pagination Text.
- Text Alignment – This allows you to choose how the text aligns: left, center, right, or justify.
- Text Color – Select the default text color palette for this module: light or dark. The default light color palette and dark color palettes can be configured in the Divi Theme Options.
- Text Shadow – Here you can apply a drop shadow to all the text inside this module. When a shadow type is selected, it will apply to all of the content, both the number and the title text.
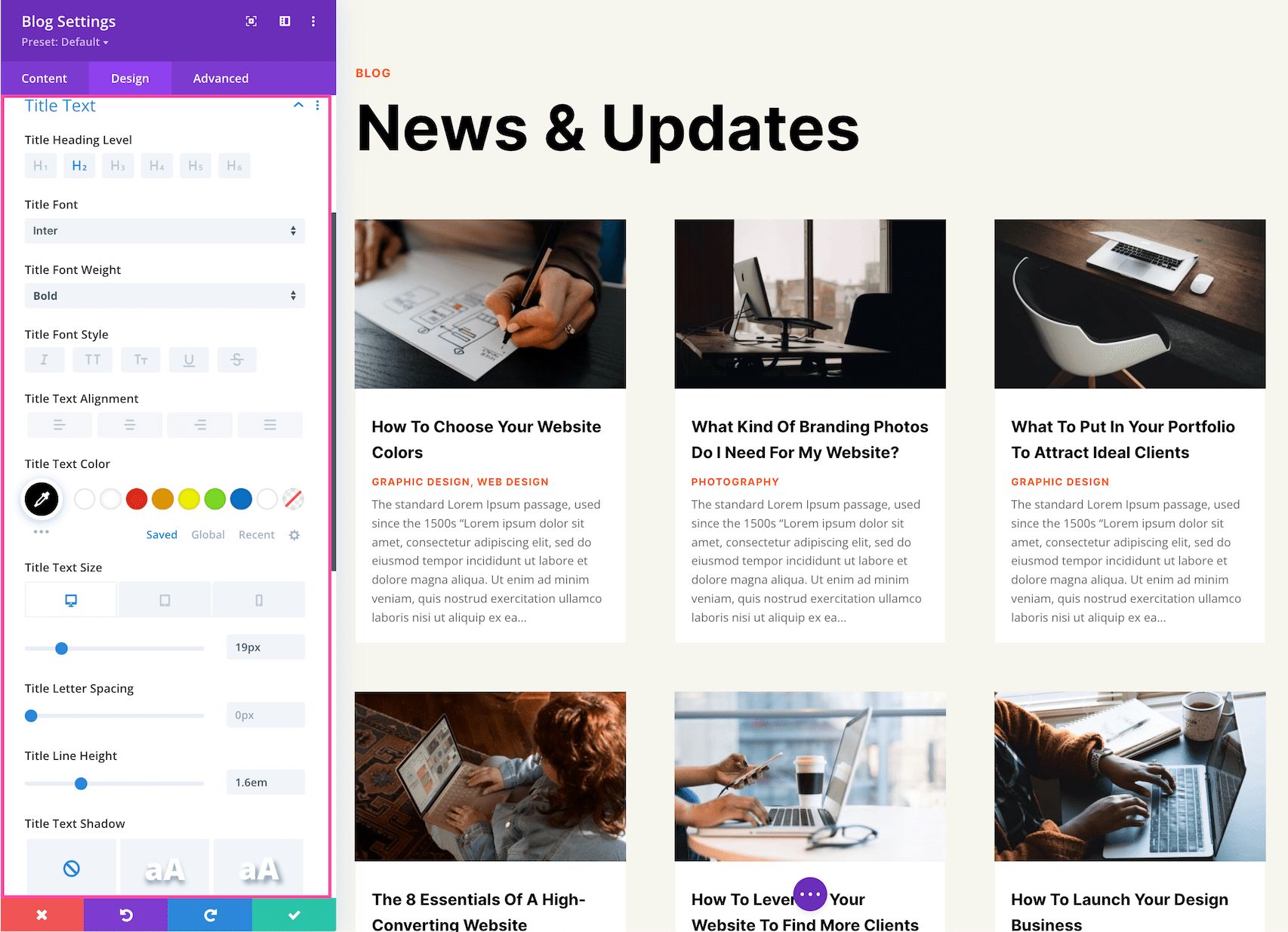
Title Text
These are the settings for specific styling and configuration for the Title Text.
- Text Heading Level – Choose the heading level you want to be assigned to the title text: h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, or h6.
- Title Font – Choose the font you want to use for the title text. The default font is automatically selected; however, you can choose a different font or upload a custom font by clicking the dropdown box.
- Title Font Weight – Click the dropdown to select the boldness of the title text font.
- Title Font Style – Choose the style of the title text font: italicized, capitalized, small capitals, underlined, or strike-through.
- Title Text Alignment – Choose the text alignment specifically to the title text only; left, center, right, or justify.
- Title Text Color – Choose a specific color for the title text. Select from your site’s color palette or click the eyedropper icon to find a new color.
- Title Text Size – Choose the font size of the title text by dragging the range slider or typing in a numerical value.
- Title Letter Spacing – Choose the letter-spacing of the title text by dragging the range slider or by typing in a numerical value. Letter spacing is the space between each individual letter. The higher the number, the more space.
- Title Line Height – Choose the line height of the title text by dragging the range slider or by typing in a numerical value. The line-height is the amount of space between each line of text. The higher the number, the more space.
- Title Text Shadow – Here you can add a drop shadow to the title text. Once a style is selected, you’ll be able to configure the direction of the shadow (horizontal and vertical), the strength of the drop shadow blur, and the shadow color.
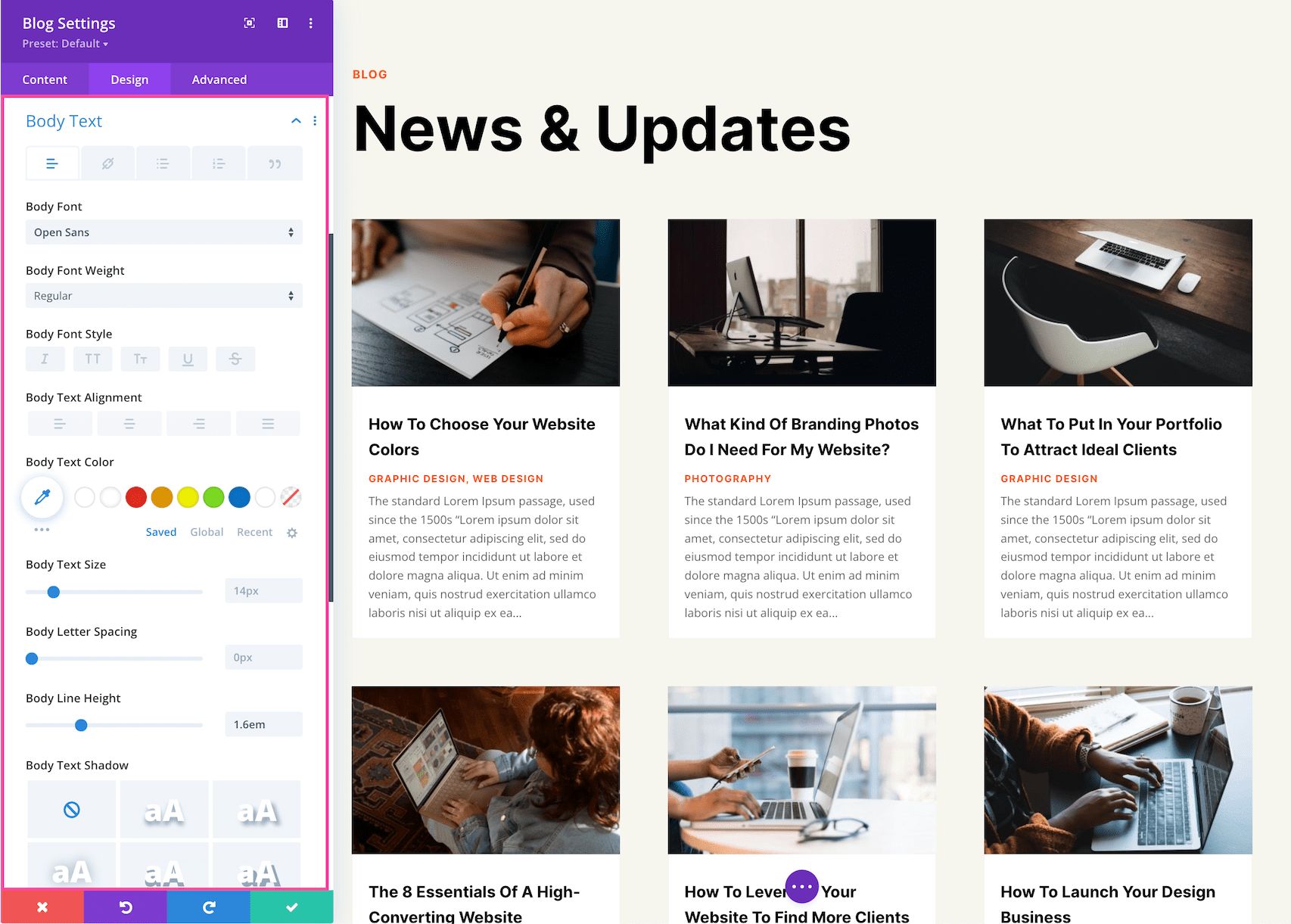
Body Text
These are the settings for specific styling and configuration for the Body Text.
- Body Font – Choose the font you want to use for the body text. The default font is automatically selected; however, you can choose a different font or upload a custom font by clicking the dropdown box.
- Body Font Weight – Click the dropdown to select the boldness of the body text font.
- Body Font Style – Choose the style of the body text font: italicized, capitalized, small capitals, underlined, or strike-through.
- Body Text Alignment – Choose the text alignment specifically to the body text only; left, center, right, or justify.
- Body Text Color – Choose a specific color for the body text. Select from your site’s color palette or click the eyedropper icon to find a new color.
- Body Text Size – Choose the font size of the body text by dragging the range slider or typing in a numerical value.
- Body Letter Spacing – Choose the letter-spacing of the body text by dragging the range slider or by typing in a numerical value. Letter spacing is the space between each individual letter. The higher the number, the more space.
- Body Line Height – Choose the line height of the body text by dragging the range slider or by typing in a numerical value. The line-height is the amount of space between each line of text. The higher the number, the more space.
- Body Text Shadow – Here you can add a drop shadow to the body text. Once a style is selected, you’ll be able to configure the direction of the shadow (horizontal and vertical), the strength of the drop shadow blur, and the shadow color.
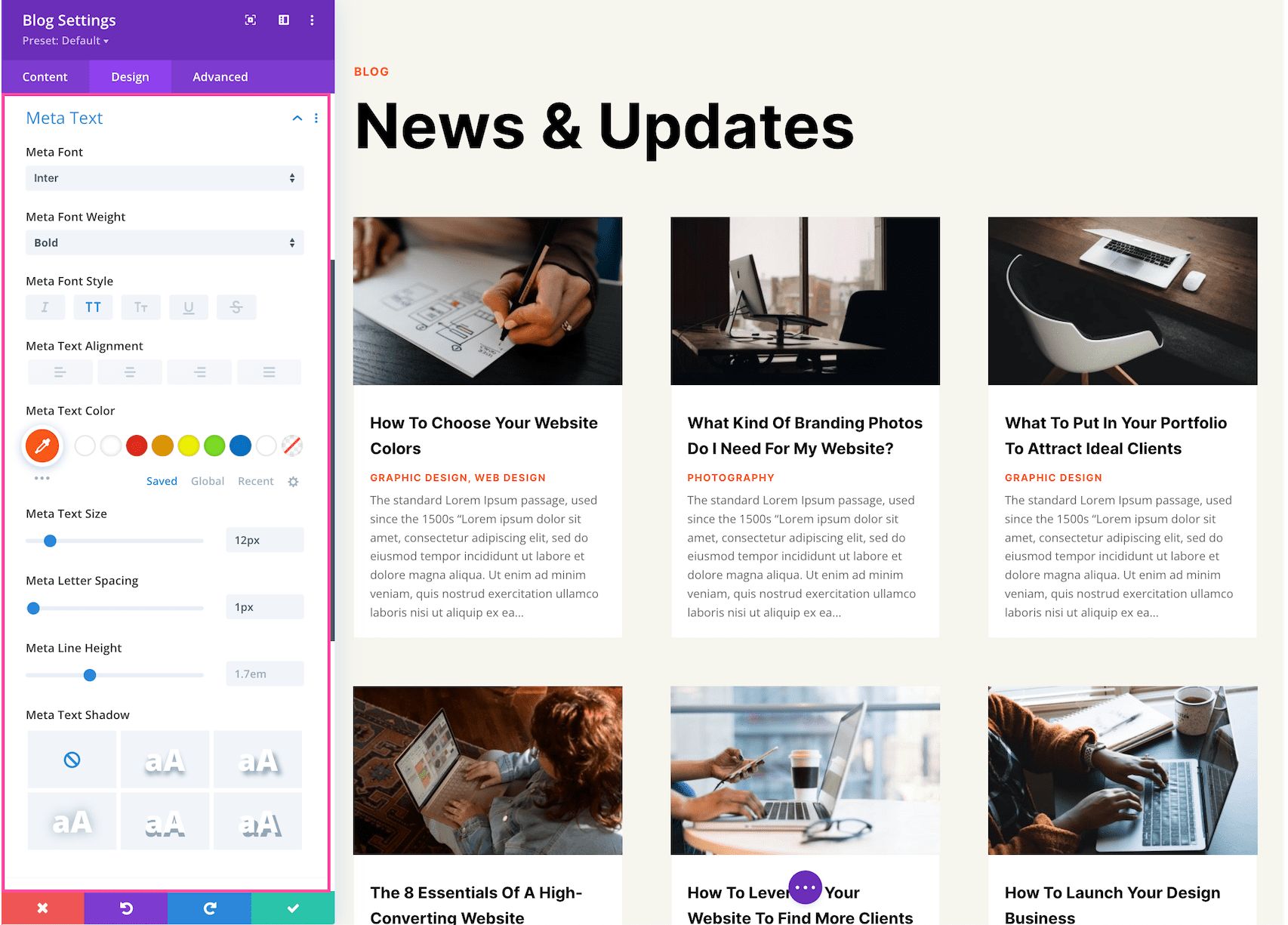
Meta Text
These are the settings for specific styling and configuration for the Meta Text only which displays the blog post info (like author name, post date, post category, and comments count).
- Meta Font – Choose the font you want to use for the meta text. The default font is automatically selected; however, you can choose a different font or upload a custom font by clicking the dropdown box.
- Meta Font Weight – Click the dropdown to select the boldness of the meta text font.
- Meta Font Style – Choose the style of the meta text font: italicized, capitalized, small capitals, underlined, or strike-through.
- Meta Text Alignment – Choose the text alignment specifically to the meta text only; left, center, right, or justify.
- Meta Text Color – Choose a specific color for the meta text. Select from your site’s color palette or click the eyedropper icon to find a new color.
- Meta Text Size – Choose the font size of the meta text by dragging the range slider or typing in a numerical value.
- Meta Letter Spacing – Choose the letter-spacing of the meta text by dragging the range slider or by typing in a numerical value. Letter spacing is the space between each individual letter. The higher the number, the more space.
- Meta Line Height – Choose the line height of the meta text by dragging the range slider or by typing in a numerical value. The line-height is the amount of space between each line of text. The higher the number, the more space.
- Meta Text Shadow – Here you can add a drop shadow to the meta text. Once a style is selected, you’ll be able to configure the direction of the shadow (horizontal and vertical), the strength of the drop shadow blur, and the shadow color.
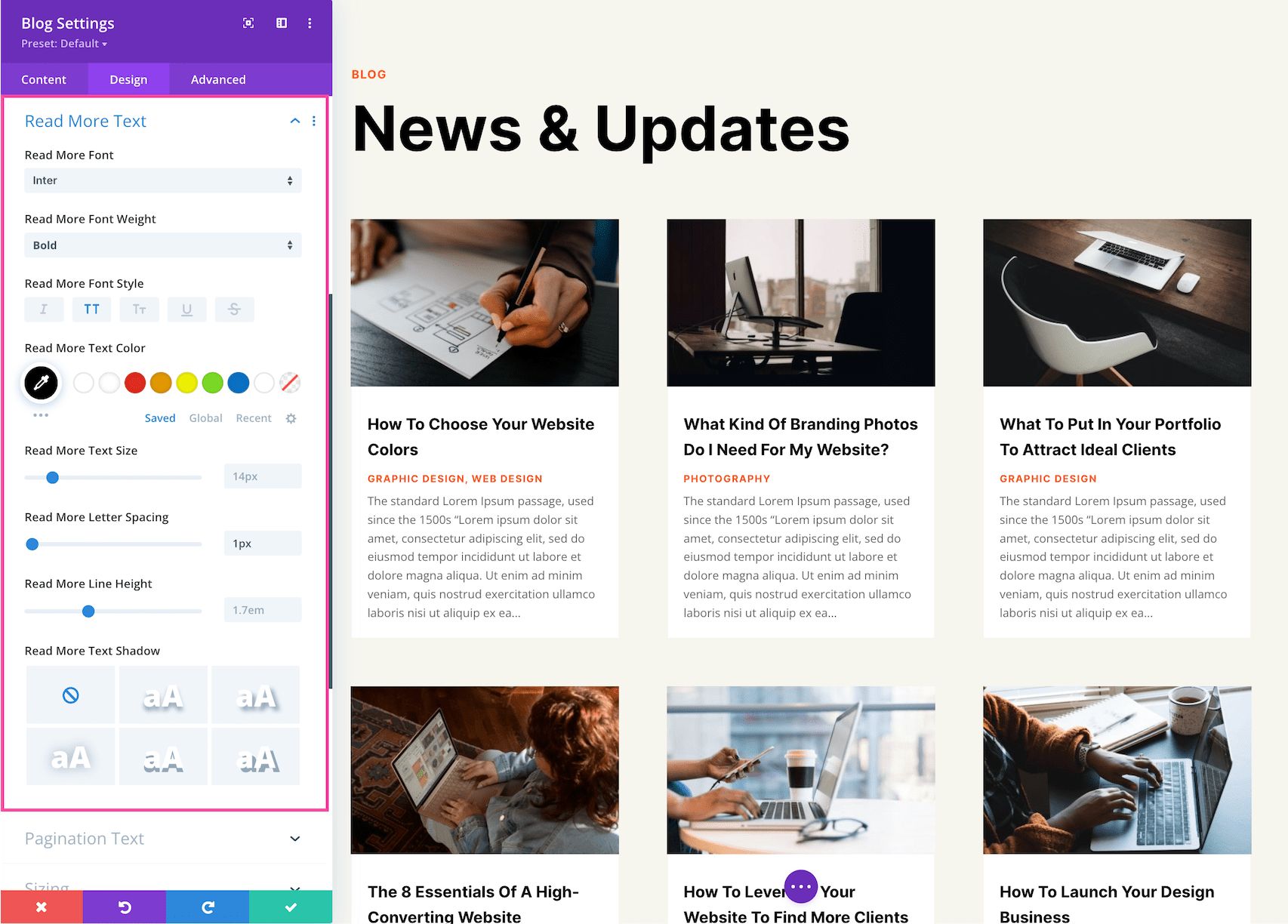
Read More Text
These are the settings for specific styling and configuration for the Read More Text only which displays the blog post info (like author name, post date, post category, and comments count).
- Read More Font – Choose the font you want to use for the read more text. The default font is automatically selected; however, you can choose a different font or upload a custom font by clicking the dropdown box.
- Read More Font Weight – Click the dropdown to select the boldness of the read more text font.
- Read More Font Style – Choose the style of the read more text font: italicized, capitalized, small capitals, underlined, or strike-through.
- Read More Text Alignment – Choose the text alignment specifically to the read more text only; left, center, right, or justify.
- Read More Text Color – Choose a specific color for the read more text. Select from your site’s color palette or click the eyedropper icon to find a new color.
- Read More Text Size – Choose the font size of the read more text by dragging the range slider or typing in a numerical value.
- Read More Letter Spacing – Choose the letter-spacing of the read more text by dragging the range slider or by typing in a numerical value. Letter spacing is the space between each individual letter. The higher the number, the more space.
- Read More Line Height – Choose the line height of the read more text by dragging the range slider or by typing in a numerical value. The line-height is the amount of space between each line of text. The higher the number, the more space.
- Read More Text Shadow – Here you can add a drop shadow to the read more text. Once a style is selected, you’ll be able to configure the direction of the shadow (horizontal and vertical), the strength of the drop shadow blur, and the shadow color.
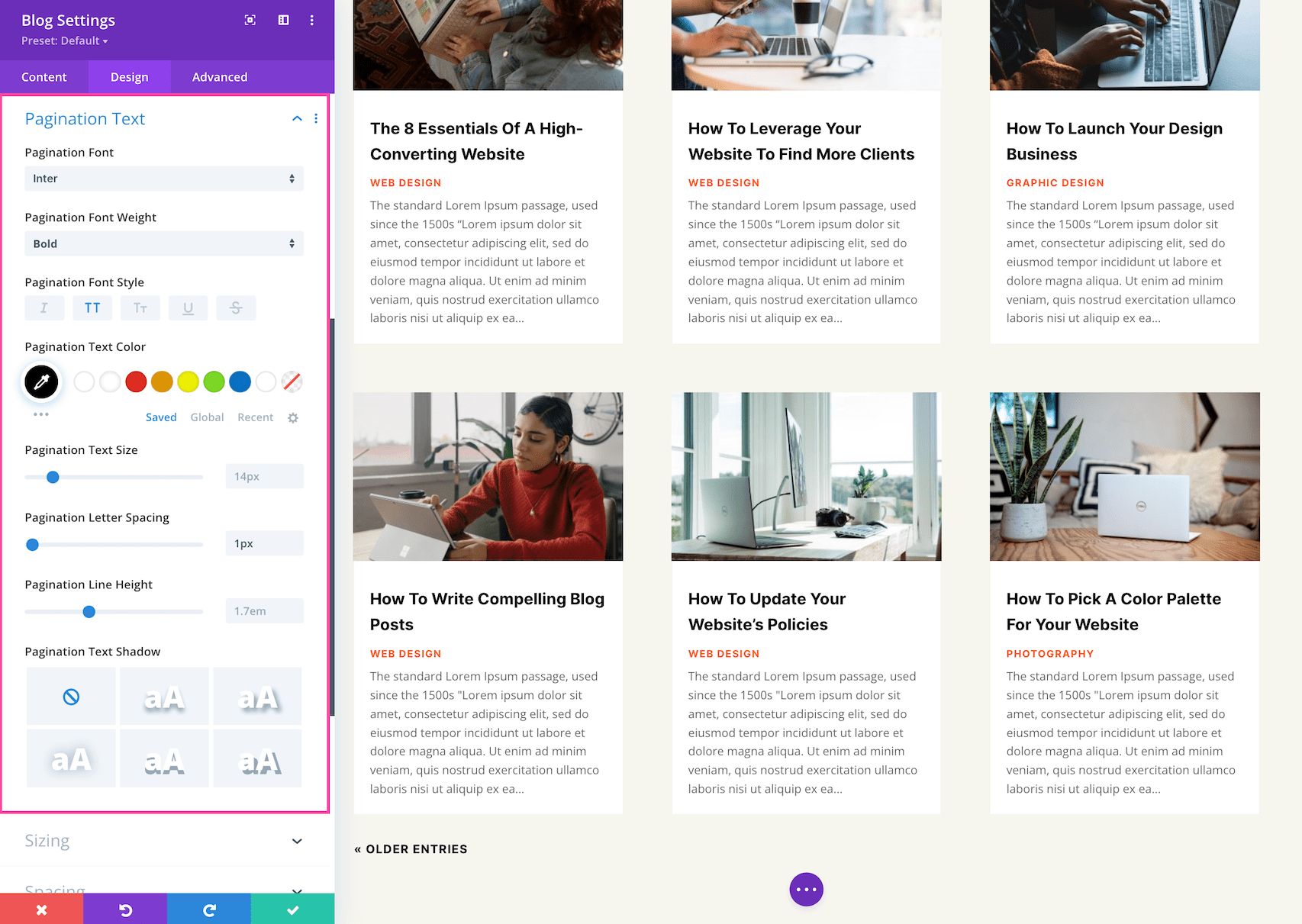
Pagination Text
These are the settings for specific styling and configuration for the Pagination Text only which displays the blog post info (like author name, post date, post category, and comments count).
- Pagination Font – Choose the font you want to use for the pagination text. The default font is automatically selected; however, you can choose a different font or upload a custom font by clicking the dropdown box.
- Pagination Font Weight – Click the dropdown to select the boldness of the pagination text font.
- Pagination Font Style – Choose the style of the pagination text font: italicized, capitalized, small capitals, underlined, or strike-through.
- Pagination Text Alignment – Choose the text alignment specifically to the pagination text only; left, center, right, or justify.
- Pagination Text Color – Choose a specific color for the pagination text. Select from your site’s color palette or click the eyedropper icon to find a new color.
- Pagination Text Size – Choose the font size of the pagination text by dragging the range slider or typing in a numerical value.
- Pagination Letter Spacing – Choose the letter-spacing of the pagination text by dragging the range slider or by typing in a numerical value. Letter spacing is the space between each individual letter. The higher the number, the more space.
- Pagination Line Height – Choose the line height of the pagination text by dragging the range slider or by typing in a numerical value. The line-height is the amount of space between each line of text. The higher the number, the more space.
- Pagination Text Shadow – Here you can add a drop shadow to the pagination text. Once a style is selected, you’ll be able to configure the direction of the shadow (horizontal and vertical), the strength of the drop shadow blur, and the shadow color.
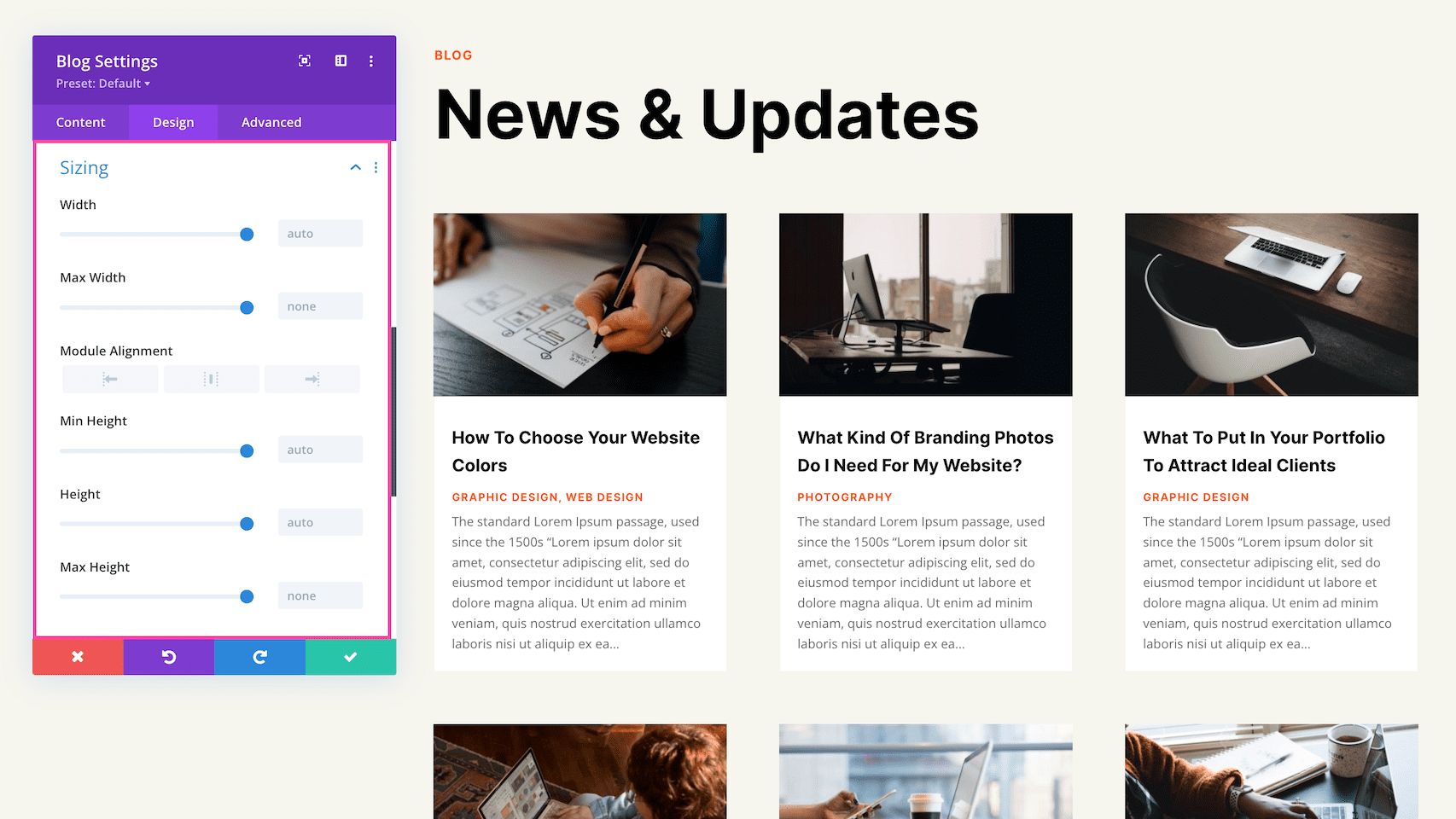
Sizing
This section defines the sizing (width and height) of the module. You can set a max-width and a max-height and a min-height for the module. Choose the module alignment (left, center, or right) by clicking the arrows. By default, modules align center.
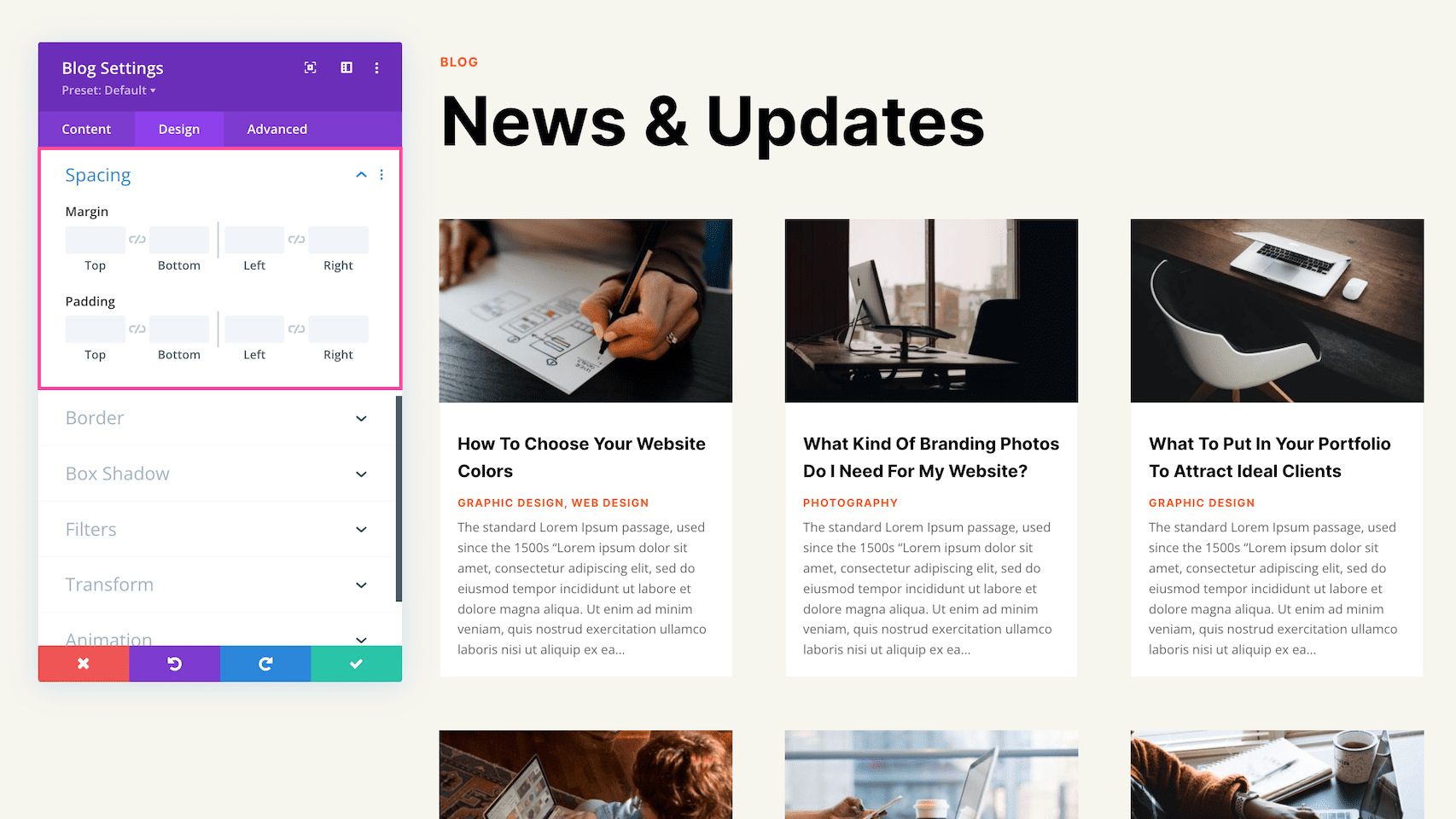
Spacing
Here is where you can add margins or spacing to this module by typing in numerical values. Margins add space outside the module element, and padding adds space inside the module element. To lock in ratios and keep the values the same, you can click the chainlink icon between the values you want to always be identical (ex: top and bottom).
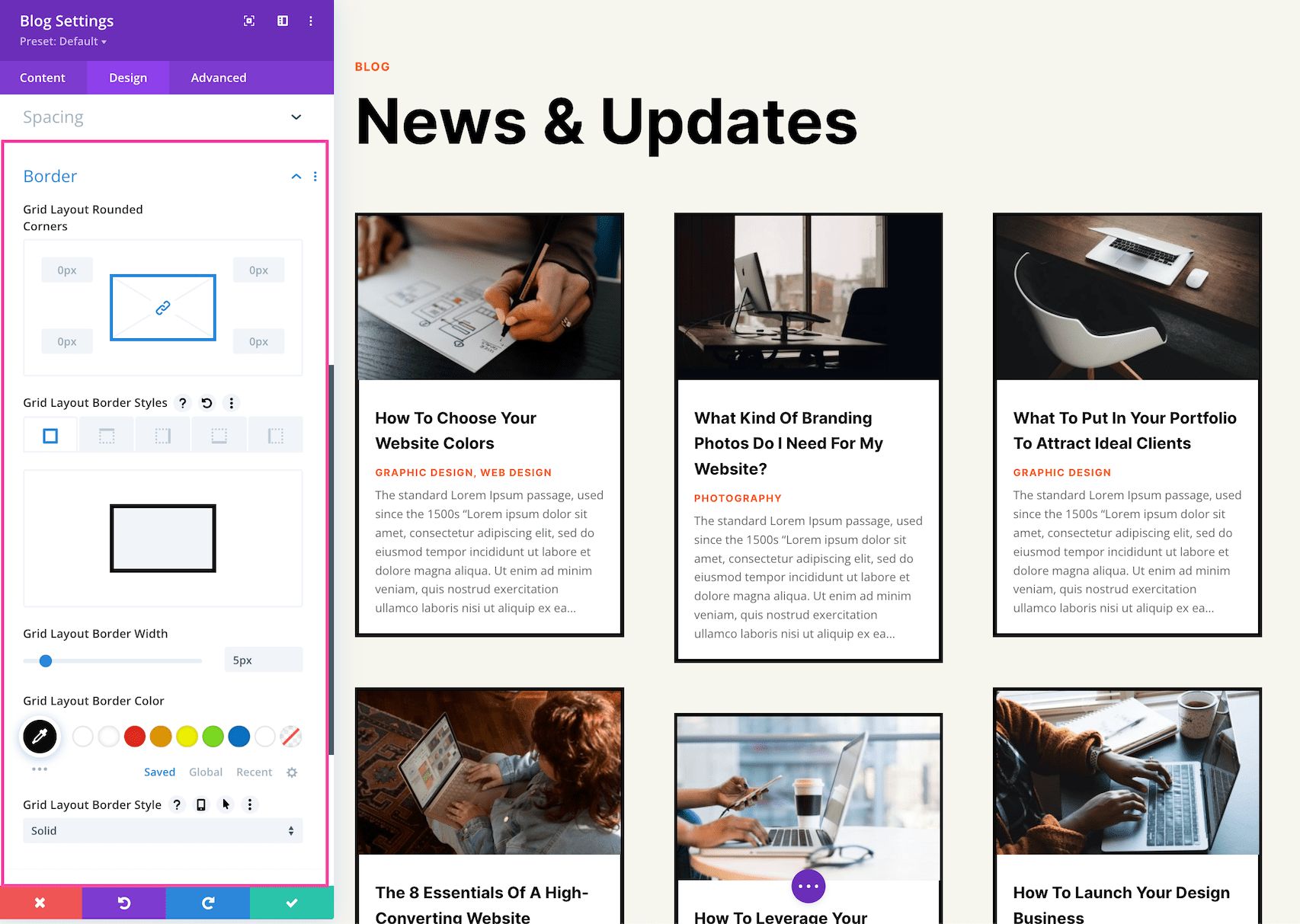
Border
This is where you can add a border to the module. When you add a border, it will add the border to the individual blog cards. To add a border surrounding the entire module, we suggest adding a border to the row containing the module.
- Rounded Corners – If you would like to have round border corners, type in a numerical value. The higher the number, the rounder the corners will be. The corner values are automatically linked (as seen by the highlighted blue chainlink in the middle) however if you’d like to have different values for each corner, simply click the blue chainlink to unlink the values. If the values are automatically linked that means they will always have the same value and update automatically if one value is changed.
- Border Styles – Here you can add a border to all sides of the module or to individual sides (top, right, bottom, and left).
- Border Width – This is where you set the width of the border. For a thicker border, increase the number. The border width must be at least 1px in order to show.
- Border Color – This is where you can pick the color of the border. You can select a color from your default site color palette already displayed, or click on the eyedropper icon to find a new color.
- Border Style – Here you can select what style of border you’d like: solid, dashed, dotted, double, groove, ridge, inset, outset, or none.
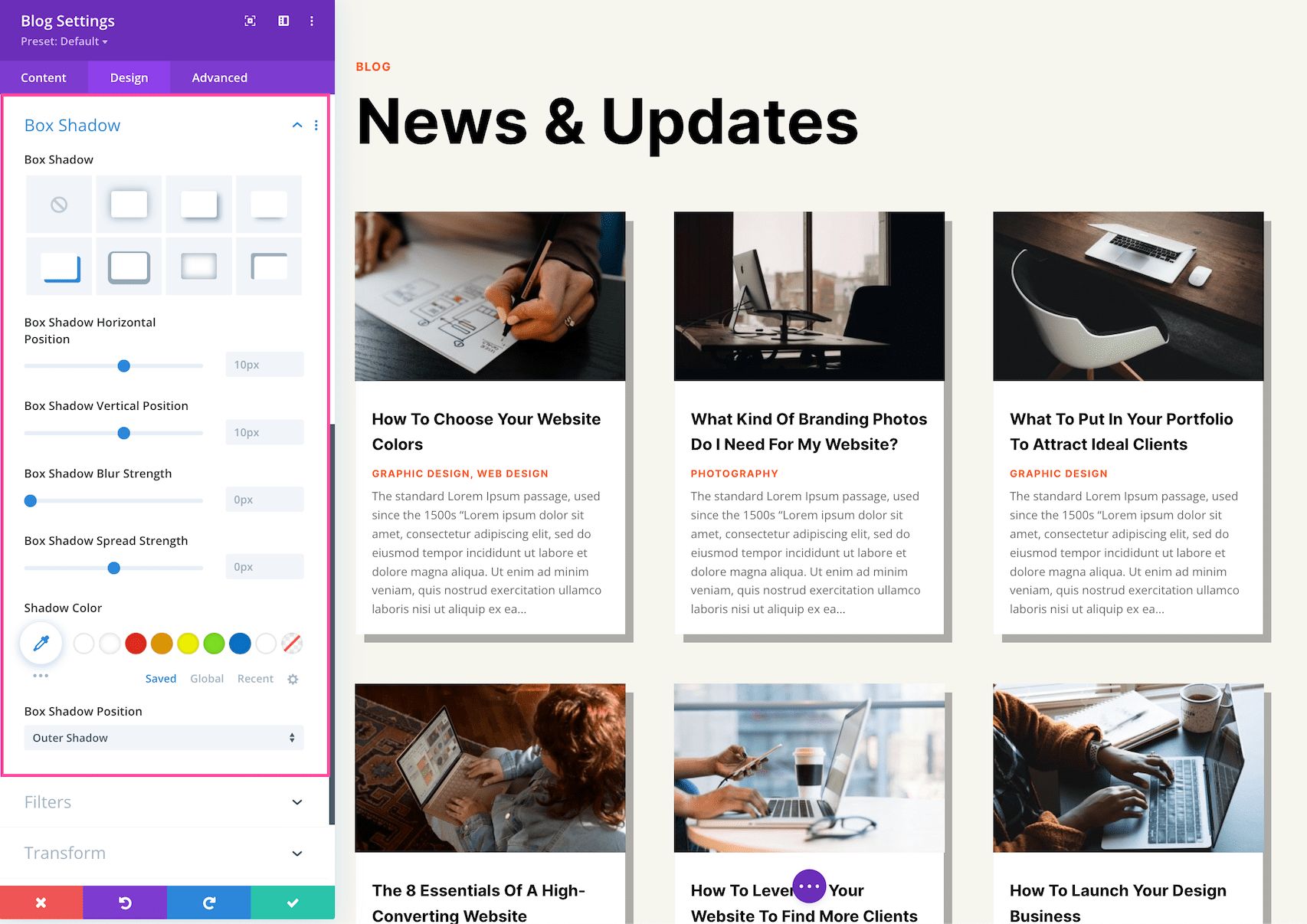
Box Shadow
Here you can add a drop shadow to the blog module which will apply a drop shadow to the individual blog cards. Once a shadow style is clicked, you can customize the position of the drop shadow (horizontal and vertical), the strength of the blur, and the spread strength by adjusting the range slider or inputting numerical values. Select the drop shadow’s color from your site’s color palette or click the eyedropper to find a new color. Choose the box-shadow position to be inside the container or outside the container via the dropdown.
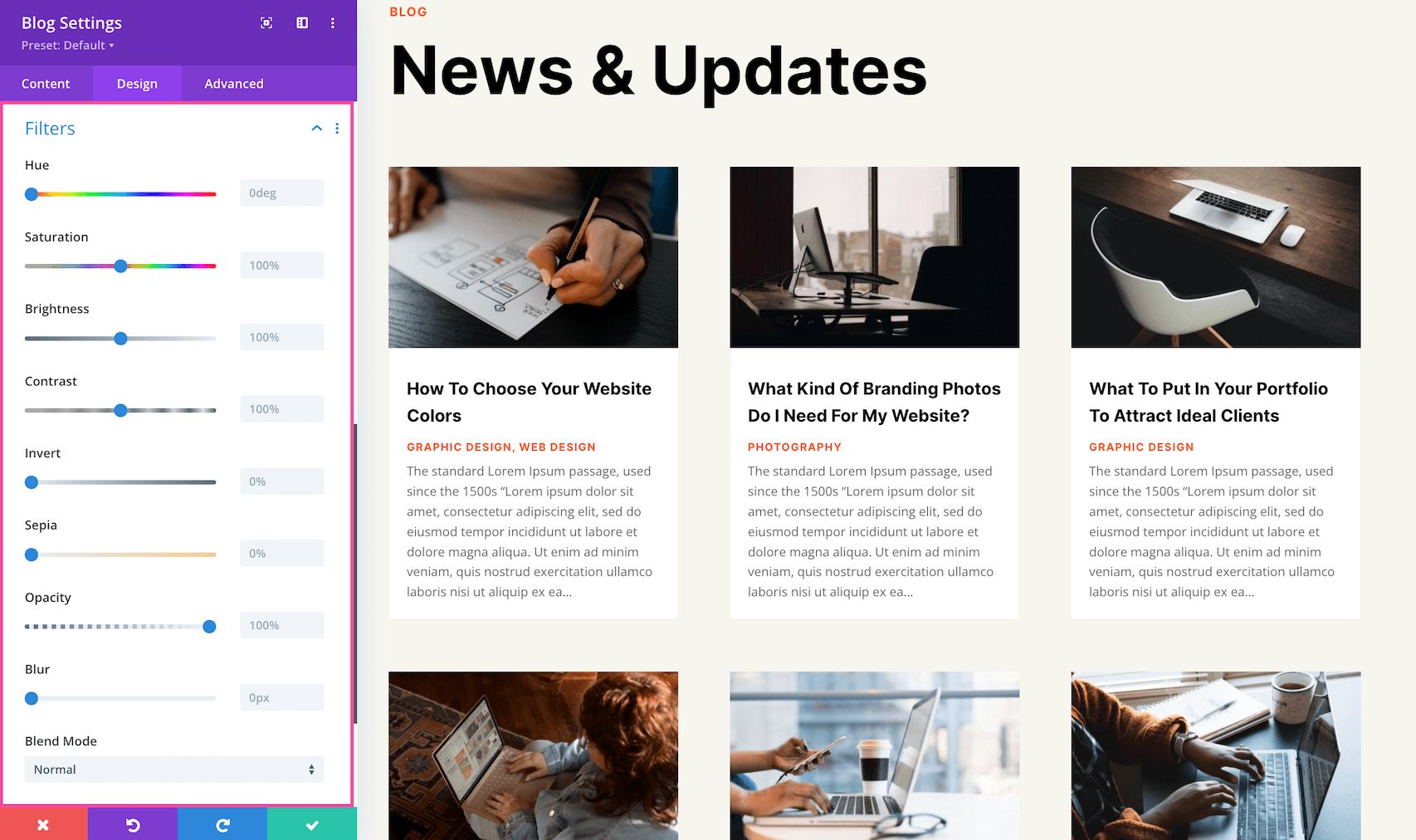
Filters
Adjust the hue, saturation, brightness, contrast, color tones (inverted colors or sepia), opacity, and blur of this module. The Blend Mode refers to how the module blends with the layers beneath it. By default, “normal” will be selected.
Transform
Scale, translate, rotate, skew, and set origin points for this module. Tab through to access each feature. Configure each feature by inputting numerical values or dragging and expanding the box or circle. You can lock in these values to always be identical by clicking the chain link icon at the bottom right.
Animation
Here you can apply animation to the module. Once you choose an option you can also adjust the duration, delay, opacity, and speed of the animation and whether you want it to continually repeat or just happen once.
Advanced
This is where the advanced customization settings are for this module.
CSS ID & Classes
This is where you can assign a specific CSS ID or class to this module. This is helpful when you’d like to apply custom CSS to a module by using your child theme’s stylesheet.
Custom CSS
You can also apply custom CSS to this module by pasting it in this tab. When you click on the Custom CSS tab, you’ll see individual sections where you can add CSS to specific elements in the module.
Conditions
This tab allows you to choose when to display this module based on a set of conditions, like what time a user is visiting the page if they’ve already purchased from your company before, what browser they are using, what operating system they’re using, and more. You can add one condition or multiple conditions by click “Add Condition”.
Visibility
This defines the visibility of the module. You can choose to disable it (hide it from view) when the display window is a Phone, Tablet, or Desktop by clicking the corresponding checkbox. You can also determine how you want overflow content to be displayed if the content overflows the element that it is in. You can choose visible, scroll, hidden, or auto for both horizontal and vertical content. By default, “auto” is selected.
Transitions
This controls the transition duration of the hover animation as well as the delay, and speed curve.
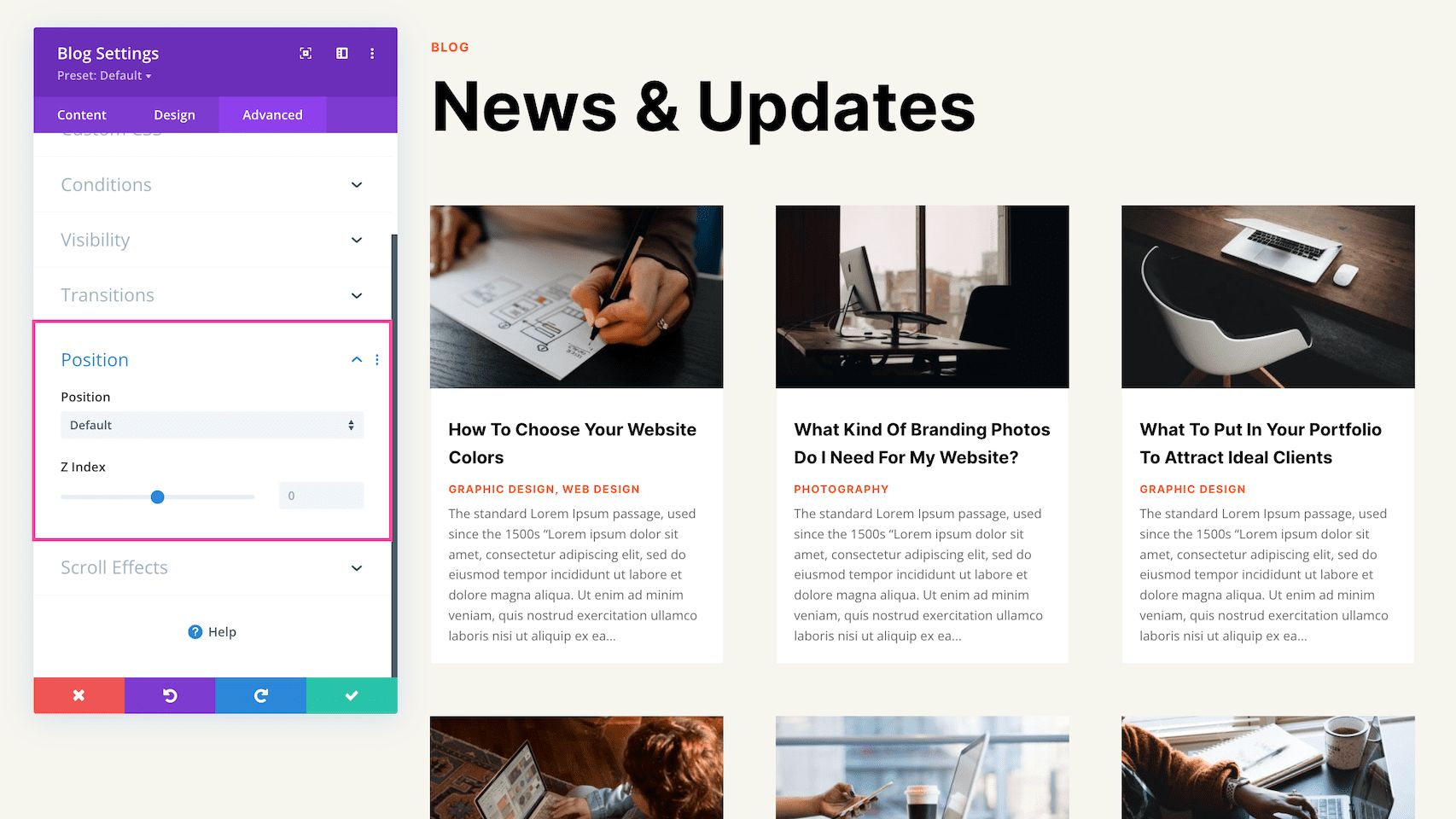
Position
This defines the position of the module as well as the offset origin, vertical and horizontal offsets, and the z-index of the module. The available positions are default (which is automatically selected), relative, absolute, and fixed. Defining the z-index allows you to specify the stack order of elements. Elements with a higher z-index number overlap elements with a lower z-index.
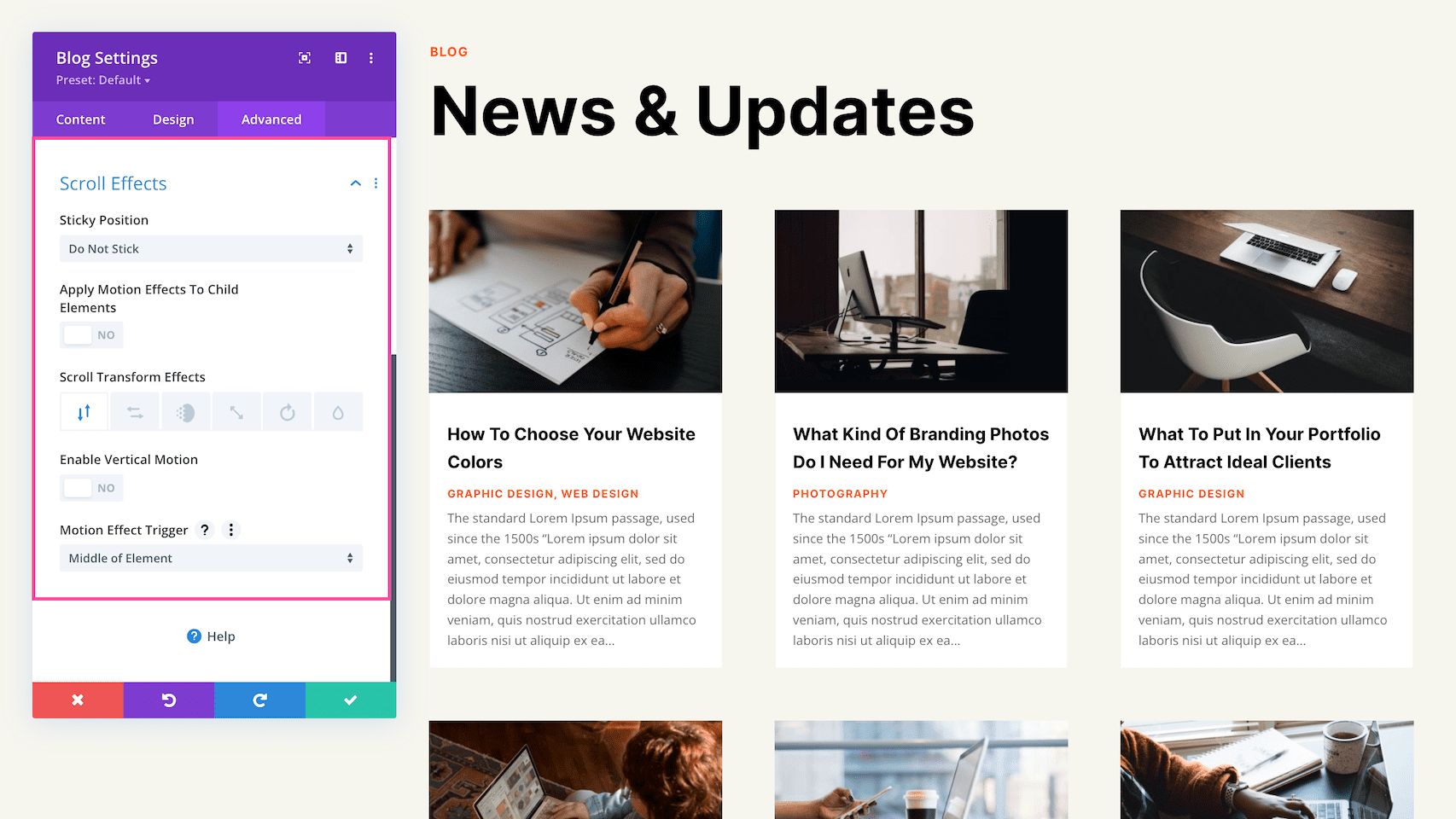
Scroll Effects
This defines how the module behaves upon scroll. You can make the module sticky (to top, bottom, or top and bottom), and choose if the module transforms upon scroll. You can also enable vertical motion on this module which allows you to adjust the speed at which this element scrolls (making it faster or slower) without affecting the surrounding elements. The Motion Trigger Effect allows you to choose when the scroll effect you just applied is triggered: when the top of the element is in view, the middle, or the bottom.
Save Your Design
Once you are finished styling and configuring the module, click the green arrow at the bottom right of the module to save your design. If you close the module without saving, your work will be lost.
Next, Save the Page Design
To save the page design, you can type CMD + S on a Mac or CTRL + S on a PC. You can also use the bottom Divi toolbar to save your page design by clicking the circle purple icon with the three dots “…” to expand the toolbar, and then clicking the green “Save” button at the bottom right.
Exit the Visual Builder
Now that all your changes are saved, click “Exit Visual Builder” on the admin toolbar at the top to exit the Visual Builder.
Tips & Best Practices for Using the Divi Blog Module
How to Design a Blog Post Template with Divi’s Theme Builder (FREE Download)
With Divi’s Theme Builder, it’s easy to create custom page templates for your blog posts. In this article, we’ll show you exactly how to do so!
Understanding the “Posts for Current Page” Option Inside the Divi Blog Module
Divi’s Blog module isn’t just for a blog page. You can also use it to build a variety of pages, like a category page or archive page. Post for Current Page is an option inside the Blog module that allows you to dynamically display posts like for a search results page, a category page, or an archive page. In this post, we’ll show you how to get that set up.
How to Add Related Posts to Your Divi Blog Post Template
Related posts are a great way to increase your blog’s traffic. Users on your blog will see posts that they’re already interested in. This keeps them on your site longer and increases their interaction with you and your website. Fortunately, related posts are easy to add to your Divi blog post templates in the Divi Theme Builder. In this article, we’ll show you how.
Continue Learning
- Browse Divi Modules Documentation
- Learn the Divi Basics
- Divi Docs
- Stay up to date with all of our latest Divi Blog tutorials by checking out our #divi-blog page.